Navigating The Network: A Comprehensive Guide To The Cranial Nerve Map
Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Cranial Nerve Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Cranial Nerve Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Cranial Nerve Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Cranial Nerve Map
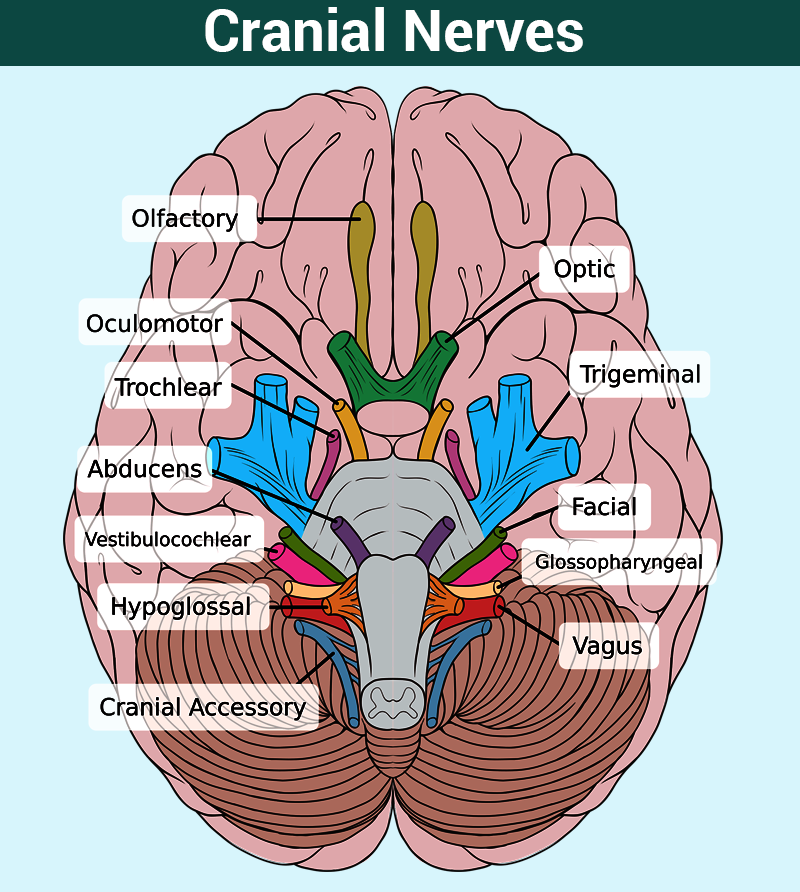
The human nervous system is a marvel of complexity, a intricate network of communication pathways that orchestrate every thought, feeling, and action. Within this vast network, a specialized group of nerves, known as cranial nerves, emerge directly from the brain, serving as vital conduits for sensory input, motor control, and autonomic functions. Understanding these nerves and their intricate map is crucial for comprehending the intricate workings of the human body and identifying potential neurological issues.
Unveiling the Cranial Nerve Map: A Detailed Exploration
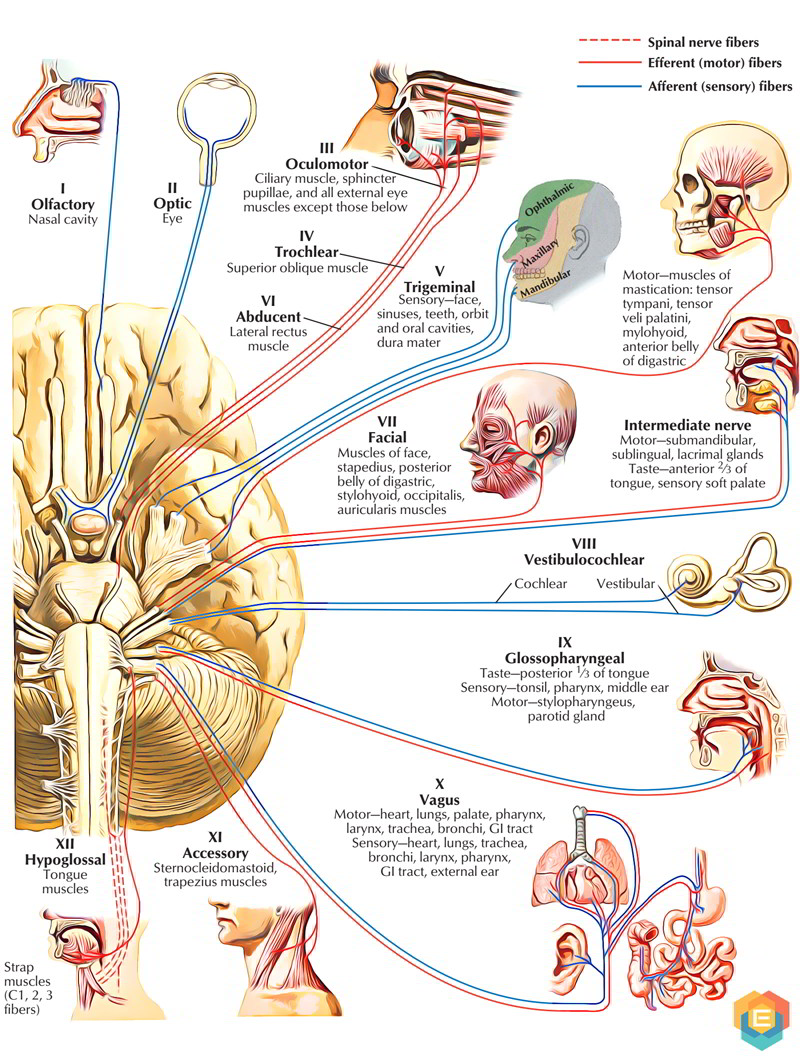
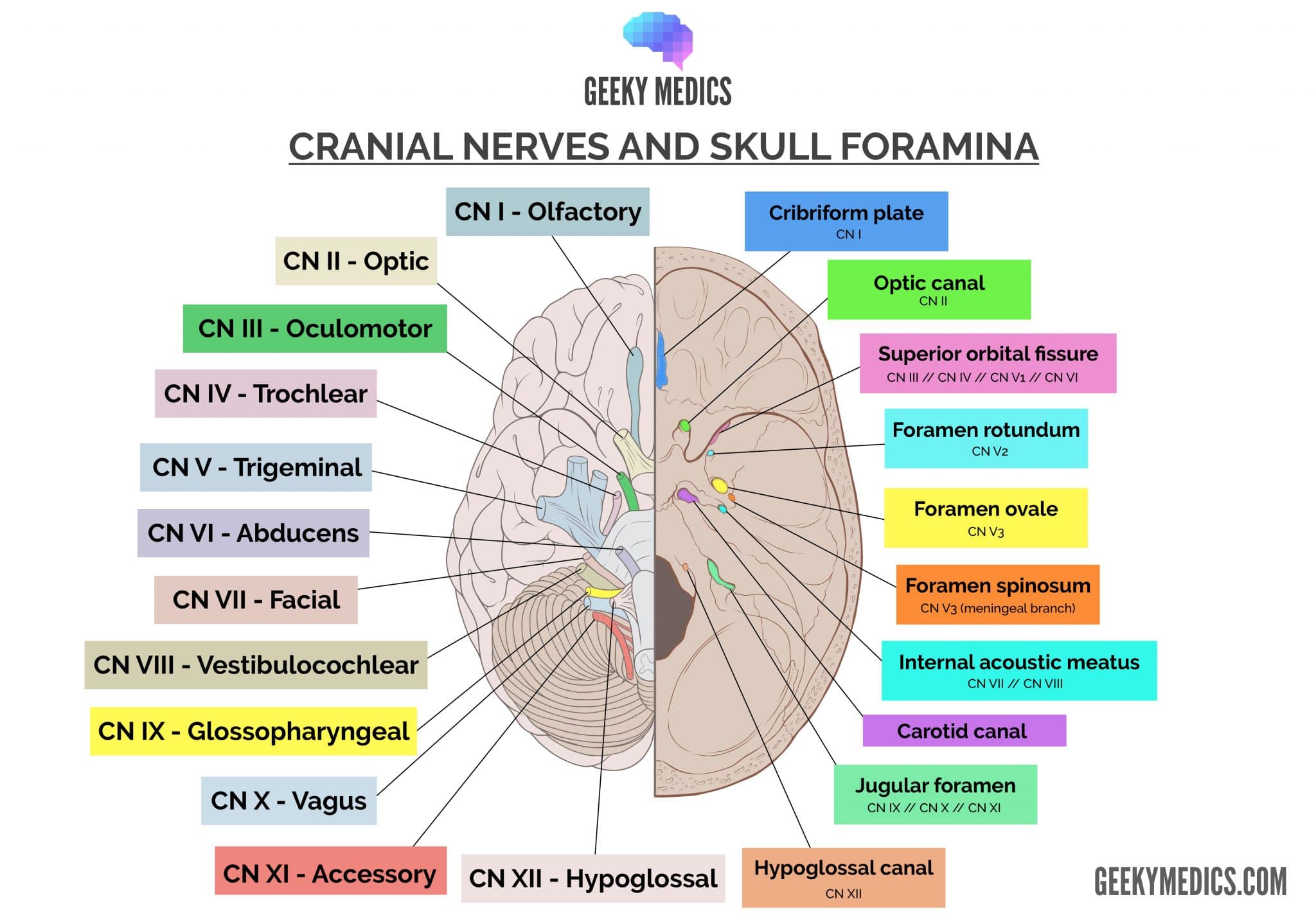
The cranial nerve map is a visual representation of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves, each designated with a Roman numeral and a descriptive name. This map serves as a guide to their anatomical location, function, and potential pathologies. Let’s delve into the details of each cranial nerve:
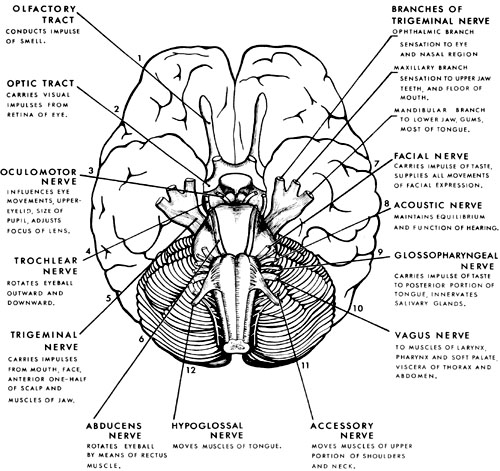
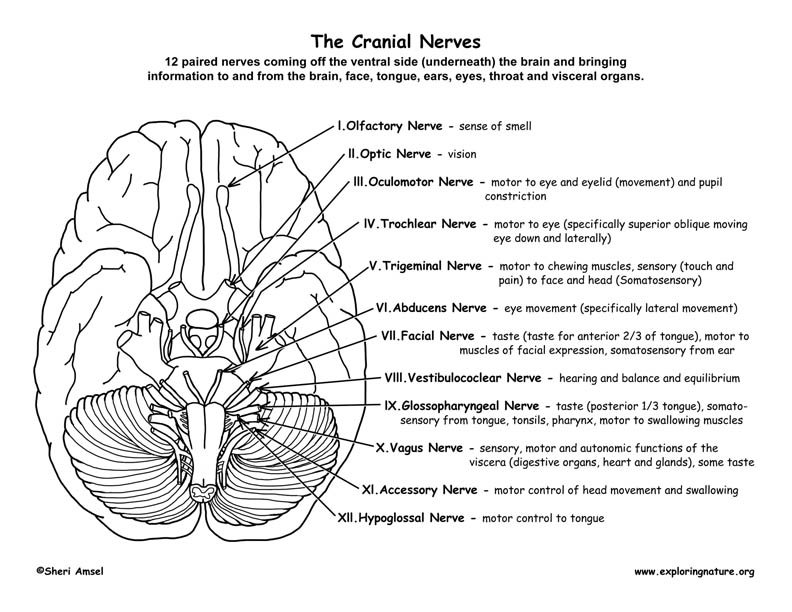
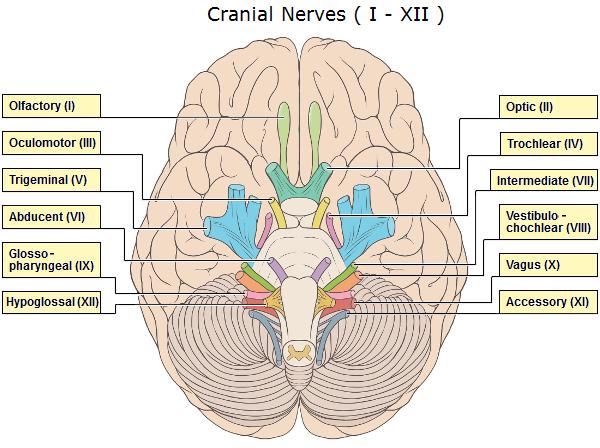
I. Olfactory Nerve: This nerve, responsible for our sense of smell, originates from the olfactory epithelium in the nasal cavity and travels to the olfactory bulb in the brain. Damage to the olfactory nerve can lead to anosmia, the inability to smell.
II. Optic Nerve: The optic nerve, responsible for vision, carries visual information from the retina to the brain. Damage to this nerve can result in visual impairments, ranging from blurred vision to complete blindness.
III. Oculomotor Nerve: This nerve controls the movement of the eye muscles (superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, inferior oblique) and the pupillary sphincter muscle, responsible for constricting the pupil. Damage to the oculomotor nerve can lead to diplopia (double vision), ptosis (drooping eyelid), and pupillary dilation.
IV. Trochlear Nerve: The trochlear nerve controls the superior oblique muscle, responsible for downward and outward eye movements. Damage to this nerve can lead to diplopia and difficulty looking down and inward.
V. Trigeminal Nerve: The trigeminal nerve is the largest cranial nerve, responsible for both sensory and motor functions. Its sensory branches innervate the face, scalp, and teeth, while its motor branches control the muscles of mastication (chewing). Damage to the trigeminal nerve can lead to facial pain, numbness, weakness in chewing, and trigeminal neuralgia, a condition characterized by intense facial pain.
VI. Abducens Nerve: The abducens nerve controls the lateral rectus muscle, responsible for outward eye movements. Damage to this nerve can lead to diplopia and difficulty looking outward.
VII. Facial Nerve: The facial nerve controls facial expressions, taste sensation on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and salivary gland secretions. Damage to this nerve can lead to facial paralysis, loss of taste, and dry mouth.
VIII. Vestibulocochlear Nerve: This nerve is responsible for hearing and balance. Its two branches, the cochlear nerve and the vestibular nerve, transmit auditory information and information about head position and movement, respectively. Damage to this nerve can lead to hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness.
IX. Glossopharyngeal Nerve: The glossopharyngeal nerve controls swallowing, taste sensation on the posterior one-third of the tongue, and salivary gland secretions. Damage to this nerve can lead to difficulty swallowing, loss of taste, and dry mouth.
X. Vagus Nerve: The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve, responsible for a wide range of functions, including heart rate regulation, breathing, digestion, and speech. Damage to this nerve can lead to a variety of symptoms, including hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, and gastrointestinal problems.
XI. Accessory Nerve: The accessory nerve controls the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, responsible for head and shoulder movements. Damage to this nerve can lead to weakness in these muscles, making it difficult to turn the head and shrug the shoulders.
XII. Hypoglossal Nerve: The hypoglossal nerve controls the tongue muscles, responsible for speech and swallowing. Damage to this nerve can lead to difficulty speaking and swallowing, as well as tongue atrophy.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Significance of Cranial Nerves
The cranial nerve map is more than just a visual representation; it is a powerful tool for understanding the intricate workings of the human body. It provides a framework for:
- Diagnosing neurological disorders: By carefully assessing the function of each cranial nerve, healthcare professionals can pinpoint the location and nature of neurological damage. This information is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Monitoring neurological recovery: The cranial nerve map allows clinicians to track the progress of patients with neurological conditions. Changes in nerve function can indicate improvement or deterioration, guiding treatment strategies.
- Understanding the impact of neurological conditions: The map helps to explain the specific symptoms associated with various neurological disorders, providing a deeper understanding of their impact on the patient’s life.
- Developing new treatments: By studying the intricate connections between cranial nerves and the brain, researchers are developing innovative treatments for neurological conditions, such as nerve stimulation therapies and stem cell therapies.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Cranial Nerves
1. How are cranial nerves different from spinal nerves?
Cranial nerves emerge directly from the brain, while spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord. Cranial nerves primarily serve the head and neck region, while spinal nerves innervate the rest of the body.
2. What are the common symptoms of cranial nerve damage?
Common symptoms include:
- Sensory loss: Numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation in the face, head, or tongue.
- Motor weakness: Difficulty moving the eyes, face, tongue, or shoulders.
- Speech and swallowing difficulties: Hoarseness, slurred speech, or difficulty swallowing.
- Hearing loss: Difficulty hearing or ringing in the ears.
- Balance problems: Dizziness, vertigo, or difficulty maintaining balance.
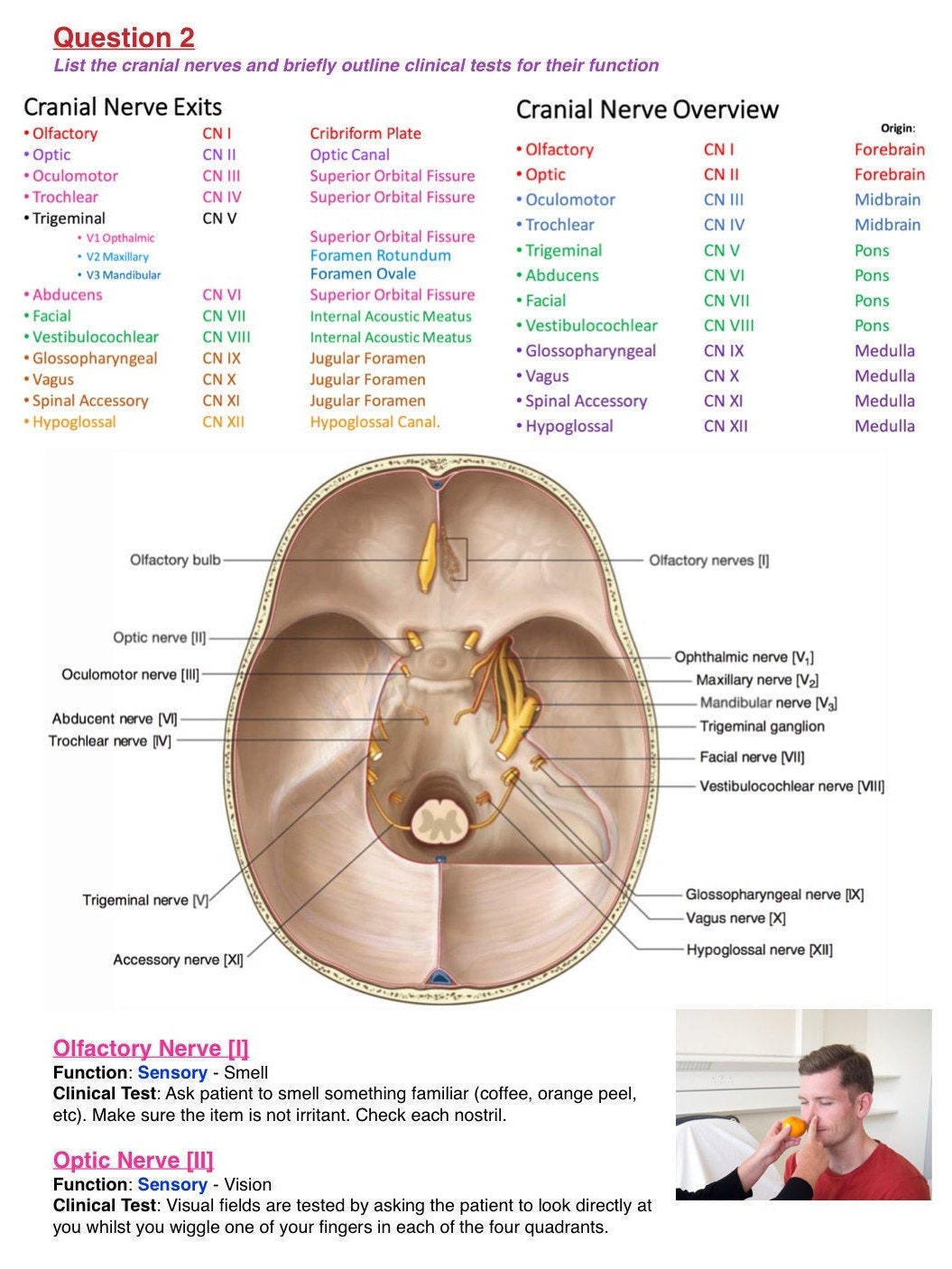
3. How are cranial nerves tested?
Cranial nerve function is assessed through a variety of clinical tests, including:
- Visual acuity tests: To assess the function of the optic nerve.
- Pupil reflex tests: To assess the function of the oculomotor nerve.
- Eye movement tests: To assess the function of the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nerves.
- Facial sensation tests: To assess the function of the trigeminal nerve.
- Facial expression tests: To assess the function of the facial nerve.
- Hearing tests: To assess the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
- Taste tests: To assess the function of the glossopharyngeal and facial nerves.
- Swallowing tests: To assess the function of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.
- Tongue movement tests: To assess the function of the hypoglossal nerve.
- Shoulder and neck movement tests: To assess the function of the accessory nerve.
4. Can cranial nerve damage be reversed?
The possibility of recovery depends on the nature and severity of the damage. Some cases of cranial nerve damage can be reversed with appropriate treatment, while others may result in permanent neurological deficits.
Tips for Maintaining Cranial Nerve Health
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can promote overall health, including the health of the nervous system.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: These habits can damage nerve cells and increase the risk of neurological problems.
- Protect your head from injury: Wearing helmets during activities such as biking, skateboarding, and skiing can reduce the risk of traumatic brain injury, which can damage cranial nerves.
- Seek medical attention for any neurological symptoms: If you experience any sudden or unexplained changes in sensation, movement, or function, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity of the Cranial Nerve Map
The cranial nerve map is a testament to the remarkable complexity and interconnectedness of the human nervous system. By understanding these vital pathways, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that govern our sensory perception, motor control, and autonomic functions. This knowledge empowers us to recognize potential neurological issues, seek appropriate medical care, and ultimately, live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cranial-nerves-2-1e3d489c9104495dbcc609ea188af32d.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Cranial Nerve Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Unraveling The Mystery: Exploring The Bermuda Triangle Through Google Maps
- The Intricate Web Of Territory: Exploring The Map Of The Warrior Cats
- Navigating The Landscape Of Gaming: A Comprehensive Guide To Casinos In New York State
- Unraveling The Secrets Of The Barren River Lake: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Ever-Evolving Landscape Of 2b2t: A Look At The 2021 Map
- Navigating The Terrain Of Conflict: Understanding The Map Of Vietnam During The War
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Fresno: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Geographic Landscape
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Medieval Spain: A Journey Through Maps
Leave a Reply