Navigating The World Of Drought: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Utilizing Drought Maps
Navigating the World of Drought: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Drought Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Drought: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Drought Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Drought: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Drought Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Drought: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Drought Maps
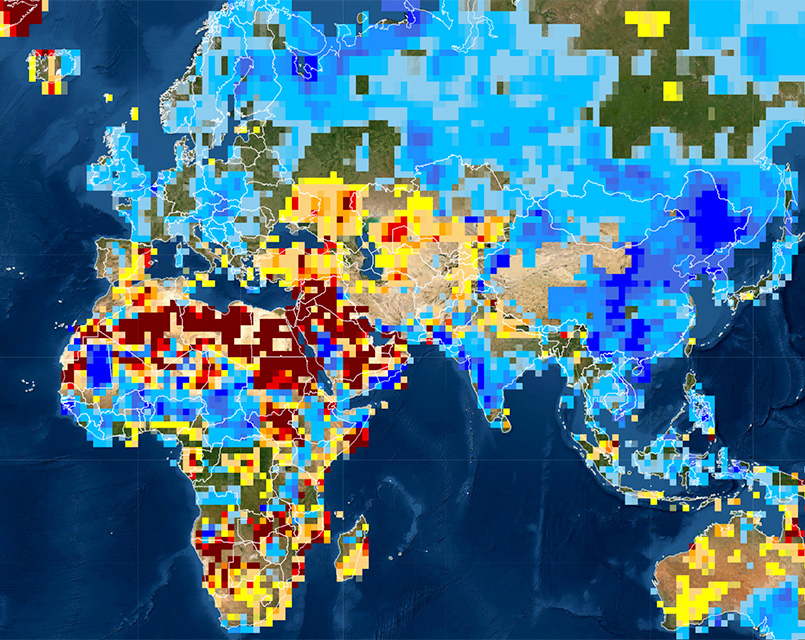
Drought, a pervasive and often devastating phenomenon, has become an increasingly significant challenge across the globe. Its impact extends far beyond the agricultural sector, affecting human health, economic stability, and environmental integrity. Understanding the nuances of drought and its spatial distribution is crucial for mitigating its effects and ensuring sustainable development. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of drought maps, exploring their intricacies, benefits, and applications.
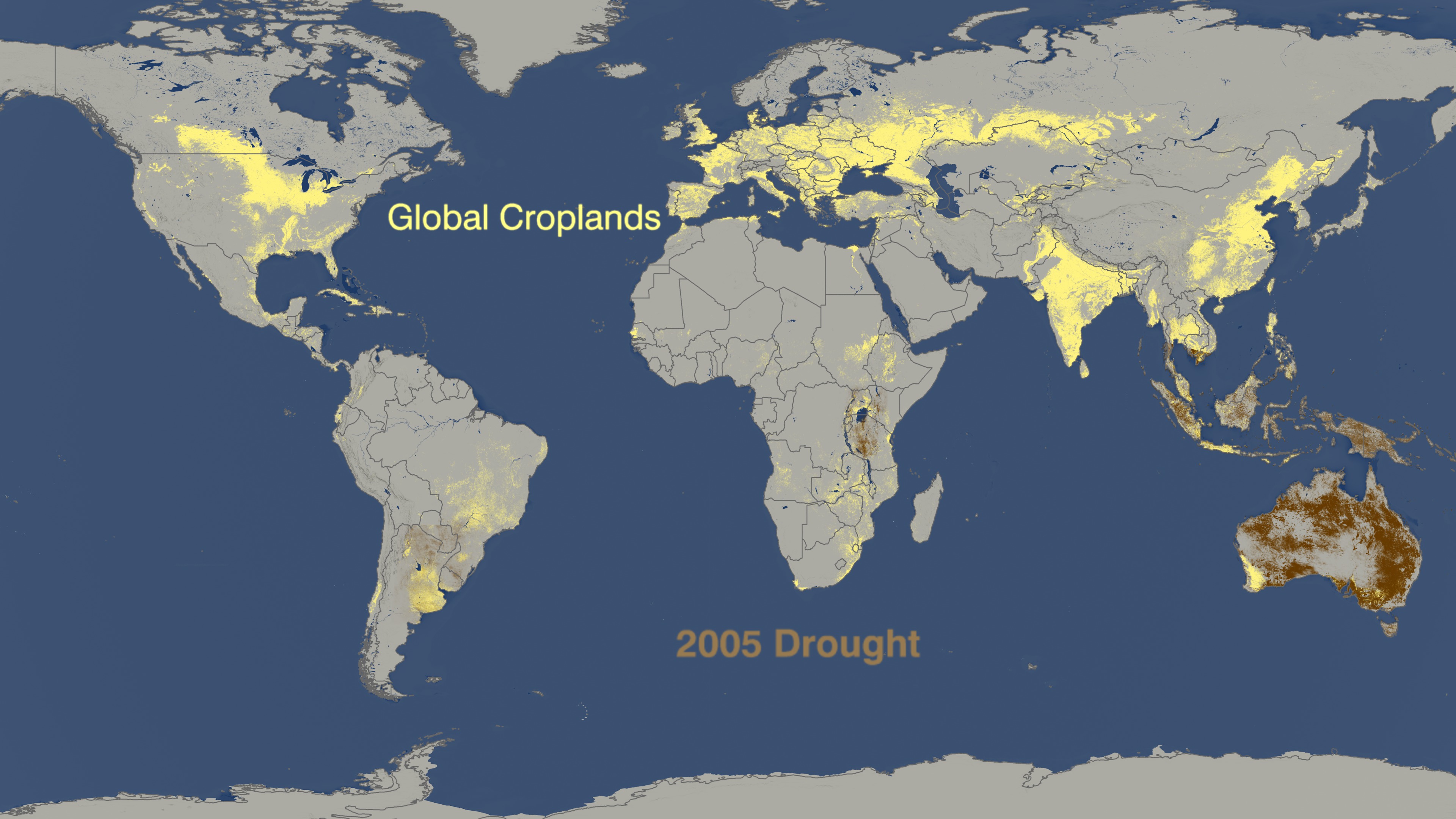
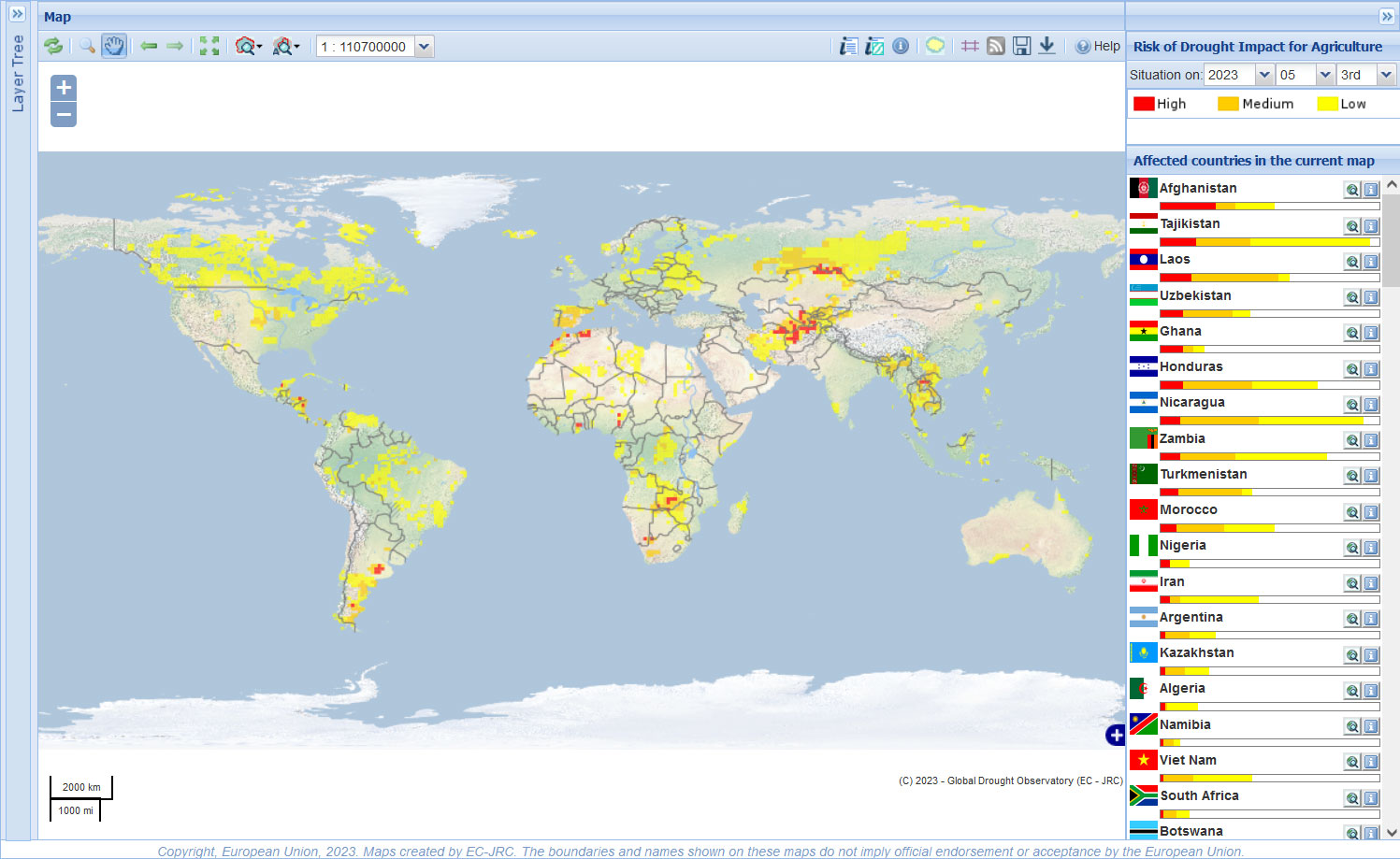
What are Drought Maps?
Drought maps are visual representations of drought conditions across geographical areas. They depict the severity and extent of drought using various indicators and data sources, providing a spatial overview of the phenomenon. These maps serve as powerful tools for monitoring, analyzing, and predicting drought events, enabling informed decision-making in response to water scarcity.
Types of Drought Maps
Drought maps can be broadly categorized based on the type of data used and the specific drought indicators they represent:
- Meteorological Drought Maps: These maps focus on precipitation deficits, depicting areas with below-average rainfall over a specific period. They utilize data from weather stations, satellite imagery, and climate models.
- Agricultural Drought Maps: These maps assess the impact of drought on agricultural productivity, considering factors like soil moisture, crop yield, and livestock water availability. They integrate data from agricultural surveys, remote sensing, and crop models.
- Hydrological Drought Maps: These maps focus on water availability in rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, depicting areas experiencing reduced water storage and flow. They utilize data from streamflow gauges, satellite observations, and hydrological models.
- Socioeconomic Drought Maps: These maps assess the social and economic impacts of drought, considering factors like food security, water access, and economic losses. They integrate data from socioeconomic surveys, market analysis, and demographic studies.
Data Sources and Methods for Creating Drought Maps
Drought maps are constructed using a variety of data sources and methods:
- Satellite Remote Sensing: Satellites provide valuable data on precipitation, soil moisture, vegetation health, and surface water bodies, enabling the monitoring of drought conditions across vast areas.
- Ground-based Observations: Weather stations, streamflow gauges, and agricultural surveys provide localized data on rainfall, water levels, and crop conditions, complementing satellite observations.
- Climate Models: These models simulate future climate scenarios, predicting potential drought occurrences and their severity, aiding in proactive drought management.
- Statistical Analysis: Statistical methods are used to analyze historical data and identify drought patterns, trends, and anomalies, contributing to the development of drought indices and maps.
Key Drought Indices Used in Mapping
Drought maps often employ specific drought indices to quantify and represent drought severity:
- Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI): This index considers precipitation, temperature, and soil moisture to assess long-term drought conditions.
- Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI): This index focuses on precipitation anomalies, considering the probability of receiving specific rainfall amounts.
- Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI): This index incorporates both precipitation and potential evapotranspiration, reflecting the overall water balance.
- Crop Moisture Index (CMI): This index measures the availability of soil moisture for crop growth, providing insights into agricultural drought.
Benefits and Applications of Drought Maps
Drought maps offer a wealth of benefits, enabling informed decision-making and effective drought management:
- Early Warning and Monitoring: Drought maps provide early warning of drought onset and track its progression, allowing for timely response and mitigation efforts.
- Resource Allocation and Management: They facilitate the efficient allocation of water resources, prioritizing areas most affected by drought and ensuring equitable distribution.
- Agricultural Planning and Mitigation: Drought maps guide farmers in making informed decisions regarding crop selection, irrigation strategies, and livestock management.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: They aid in assessing drought vulnerability, identifying high-risk areas, and developing effective disaster preparedness plans.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Drought maps contribute to understanding the impacts of climate change on drought frequency and severity, guiding adaptation strategies.
- Policy Development and Implementation: They provide valuable data for policymakers to develop and implement effective drought management policies and programs.
Challenges and Limitations of Drought Maps
Despite their numerous benefits, drought maps face certain challenges and limitations:
- Data Availability and Quality: The accuracy and reliability of drought maps depend on the availability and quality of data, which can be limited in certain regions.
- Spatial Resolution: The spatial resolution of data sources can influence the accuracy of drought maps, particularly in areas with complex topography or diverse land cover.
- Temporal Variability: Drought conditions can change rapidly, requiring frequent updates of drought maps to ensure their relevance.
- Data Integration and Interpretation: Integrating data from different sources and interpreting the complex relationships between drought indicators can be challenging.
FAQs About Drought Maps
Q: How often are drought maps updated?
A: The frequency of updates varies depending on the data sources and the specific drought index used. Some maps are updated daily, while others are updated weekly, monthly, or even seasonally.
Q: Are drought maps always accurate?
A: Drought maps are tools based on available data and models, and their accuracy can be influenced by data quality, spatial resolution, and the complexity of drought processes.
Q: How can I access drought maps?
A: Various government agencies, research institutions, and international organizations provide access to drought maps online. Specific resources can be found through searches using keywords like "drought map," "drought monitor," or "drought index."
Q: How can drought maps be used for water management?
A: Drought maps can help water managers identify areas experiencing water scarcity, prioritize water allocation, and implement water conservation measures.
Tips for Using Drought Maps Effectively
- Understand the limitations of the map: Be aware of the data sources, spatial resolution, and update frequency of the map.
- Consult multiple sources: Compare different drought maps and indices to gain a comprehensive understanding of drought conditions.
- Consider local context: Factor in local factors like soil type, land use, and water demand when interpreting drought maps.
- Use maps as a tool for communication: Share drought maps with stakeholders to raise awareness and promote collaborative action.
- Integrate maps with other data sources: Combine drought maps with other relevant data, such as agricultural statistics, socioeconomic indicators, and climate projections.
Conclusion
Drought maps are invaluable tools for understanding, monitoring, and managing drought events. They provide a visual representation of drought conditions, enabling informed decision-making across various sectors. By leveraging the insights provided by drought maps, communities, governments, and organizations can effectively mitigate the impacts of drought, promote sustainable water management, and build resilience to this pressing global challenge. Continued advancements in data collection, modeling, and visualization techniques will further enhance the accuracy and utility of drought maps, contributing to a more drought-resilient future.
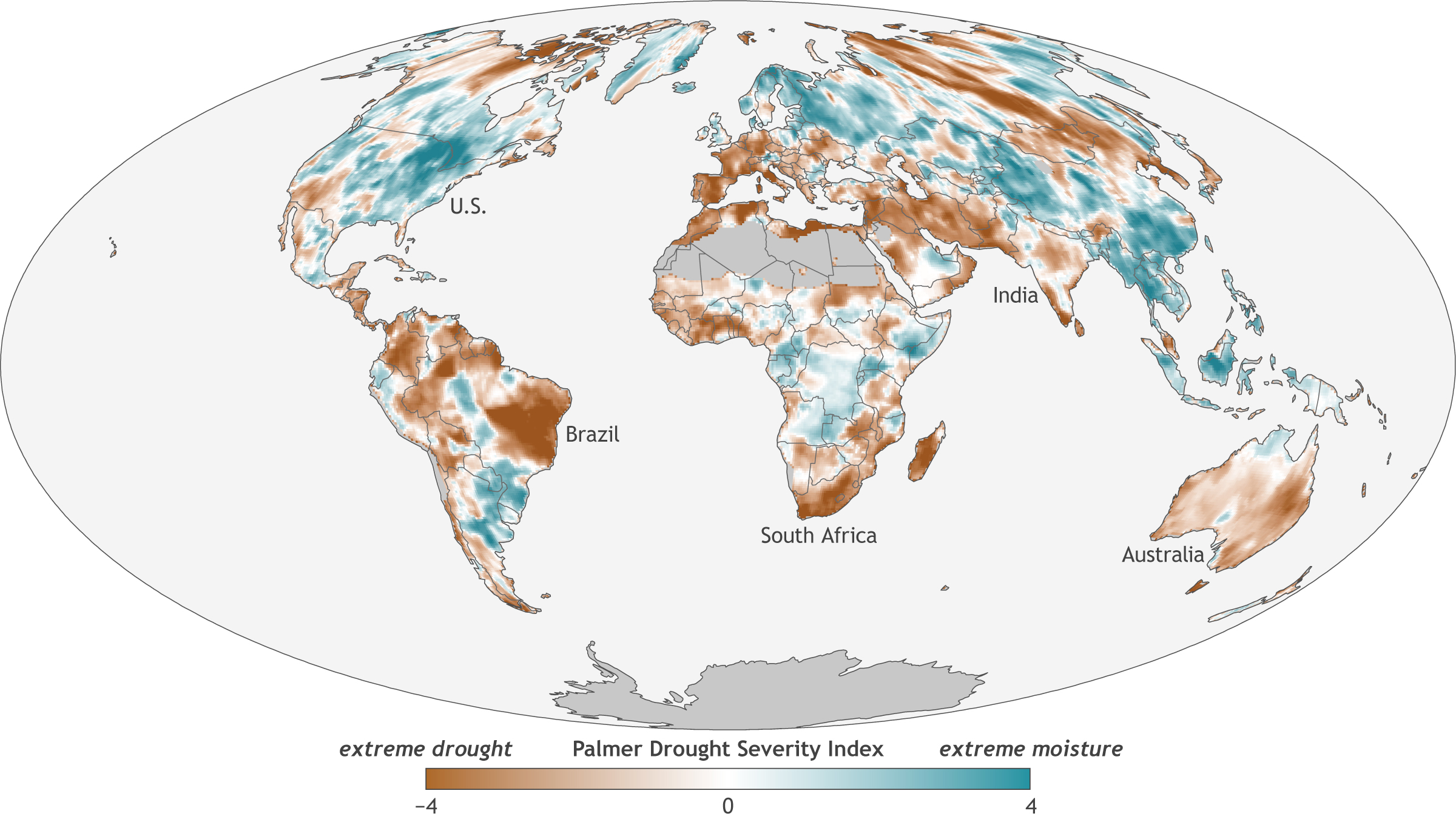
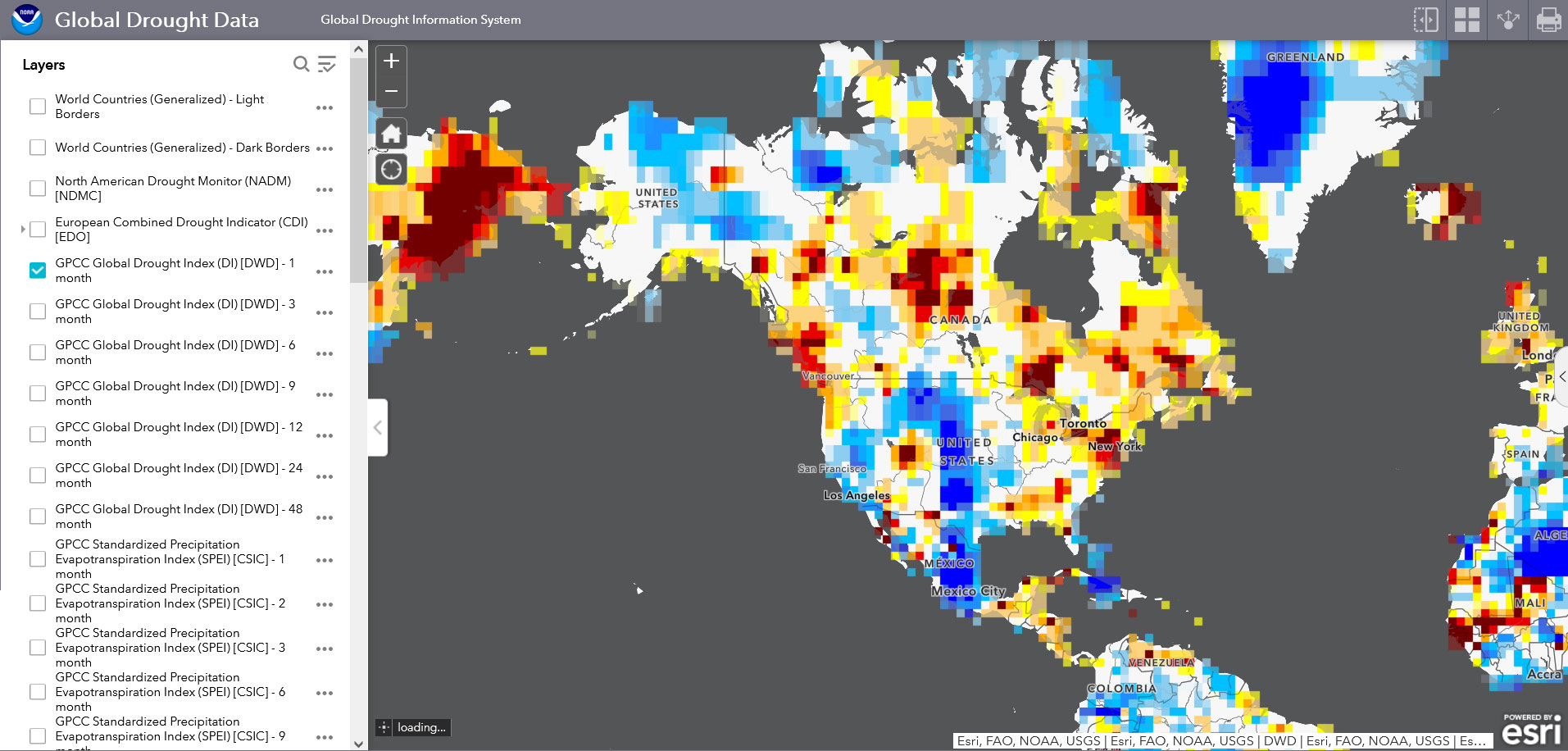
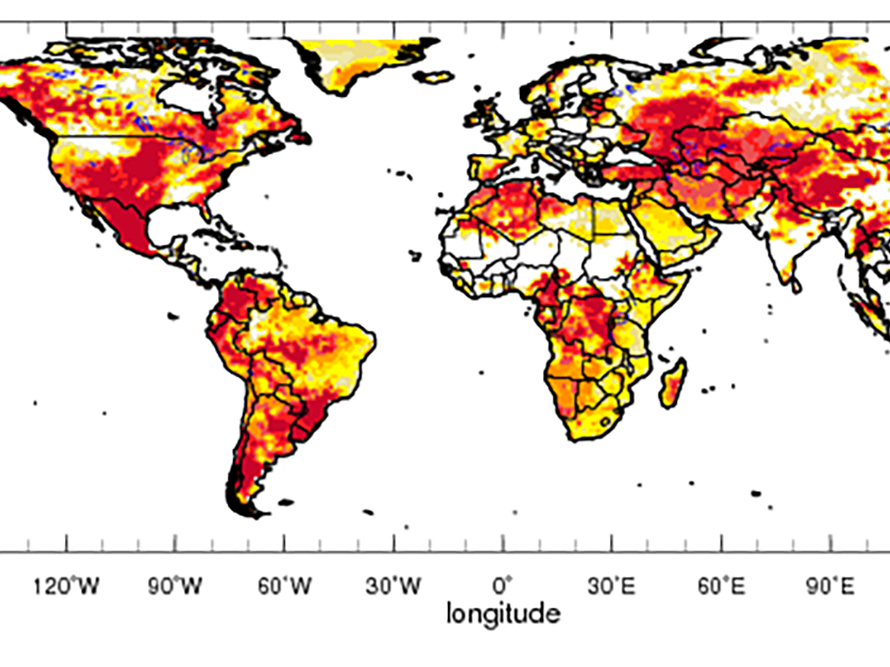



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Drought: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Drought Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Unraveling The Mystery: Exploring The Bermuda Triangle Through Google Maps
- The Intricate Web Of Territory: Exploring The Map Of The Warrior Cats
- Navigating The Landscape Of Gaming: A Comprehensive Guide To Casinos In New York State
- Unraveling The Secrets Of The Barren River Lake: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Ever-Evolving Landscape Of 2b2t: A Look At The 2021 Map
- Navigating The Terrain Of Conflict: Understanding The Map Of Vietnam During The War
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Fresno: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Geographic Landscape
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Medieval Spain: A Journey Through Maps
Leave a Reply