The Impact Of JavaScript Size On Web Mapping Performance
The Impact of JavaScript Size on Web Mapping Performance
Related Articles: The Impact of JavaScript Size on Web Mapping Performance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Impact of JavaScript Size on Web Mapping Performance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Impact of JavaScript Size on Web Mapping Performance

In the realm of web development, interactive maps are a powerful tool for enhancing user engagement and providing valuable information. JavaScript, a ubiquitous programming language, is the backbone of these dynamic maps, enabling features like zooming, panning, and data visualization. However, the size of the JavaScript code used to render these maps can significantly impact their performance, influencing user experience and website load times.
Understanding the Relationship Between JavaScript Size and Performance
The size of JavaScript files directly affects the time it takes for a web page to load. Larger JavaScript files require more time to download and parse, leading to longer loading times. This delay can be detrimental to user experience, as users may abandon a website if it takes too long to load. Moreover, slow loading times can negatively impact search engine optimization (SEO), as search engines prioritize websites with faster loading speeds.
Factors Influencing JavaScript Size
Several factors contribute to the size of JavaScript code used for web mapping:
- Library Choice: Different mapping libraries, such as Leaflet, Google Maps API, or Mapbox GL JS, vary in their size and feature sets. Choosing a library optimized for the specific map functionality required can help minimize JavaScript size.
- Feature Implementation: The complexity of the map and the features implemented directly impact the amount of JavaScript code needed. Features like custom markers, data overlays, and interactive elements contribute to the overall size.
- Code Optimization: Efficient coding practices, such as minimizing unused code and optimizing algorithms, can significantly reduce the size of the JavaScript code.
- Third-Party Libraries: Including external libraries for additional features, such as data visualization or user interaction, can increase the overall JavaScript size.
Strategies for Optimizing JavaScript Size
Several strategies can be employed to minimize the impact of JavaScript size on web mapping performance:
- Choose the Right Mapping Library: Selecting a mapping library that balances features with performance is crucial. Consider the specific requirements of the map and choose a library that provides the necessary features without unnecessary bloat.
-
Code Optimization: Implement best practices for JavaScript code optimization, such as:
- Minification: Removing unnecessary whitespace and comments from code to reduce file size.
- Code Splitting: Dividing large JavaScript files into smaller modules that load only when needed, reducing initial load time.
- Tree Shaking: Removing unused code during the build process, ensuring only necessary code is included in the final bundle.
- Lazy Loading: Delay loading non-essential JavaScript code until it is required, improving initial load times.
- Caching: Utilize browser caching to store JavaScript files locally, reducing the need to download them repeatedly.
- Compression: Employ compression techniques like GZIP to reduce the size of JavaScript files during transmission.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Leverage CDNs to distribute JavaScript files from geographically dispersed servers, reducing latency and improving download speeds.
Impact of JavaScript Size on User Experience
Optimizing JavaScript size directly impacts user experience in several ways:
- Faster Load Times: Smaller JavaScript files lead to faster page load times, enhancing user satisfaction and reducing bounce rates.
- Improved Interactivity: Reduced load times enable faster map rendering and smoother interactions, improving the overall user experience.
- Reduced Resource Consumption: Smaller JavaScript files require less memory and processing power, improving website performance and reducing resource consumption.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Faster loading times and improved interactivity benefit users with slower internet connections or limited device resources.
FAQs
Q: What are the common JavaScript mapping libraries and their size differences?
A: Popular JavaScript mapping libraries include:
- Leaflet: Lightweight and flexible, with a relatively small file size.
- Google Maps API: Offers a wide range of features but can be larger in size, especially when using advanced features.
- Mapbox GL JS: Provides high-performance and customizable maps, with a larger file size compared to Leaflet.
The specific file size varies depending on the version and included features.
Q: How can I measure the size of my JavaScript code?
A: You can use developer tools in your browser to inspect the size of JavaScript files. In Chrome, open the "Network" tab in the developer tools and analyze the "Size" column for JavaScript files.
Q: What are the best practices for optimizing JavaScript code for web mapping?
A: Best practices include:
- Minification: Use tools like UglifyJS or Terser to remove unnecessary whitespace and comments from your JavaScript code.
- Code Splitting: Break down large JavaScript files into smaller modules that load only when needed.
- Tree Shaking: Use tools like Webpack or Rollup to remove unused code during the build process.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading techniques to delay loading non-essential JavaScript code.
Tips
- Prioritize Performance: Always prioritize performance when choosing mapping libraries and implementing features.
- Measure and Monitor: Regularly measure the size of your JavaScript code and monitor its impact on website performance.
- Experiment and Optimize: Experiment with different optimization techniques and strategies to find the best approach for your specific use case.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest best practices and tools for JavaScript optimization.
Conclusion
The size of JavaScript code used for web mapping plays a crucial role in website performance and user experience. Optimizing JavaScript size through careful library selection, code optimization, and efficient loading strategies is essential for creating fast, interactive, and engaging maps. By prioritizing performance and employing best practices, developers can ensure their web maps deliver a seamless and positive user experience.
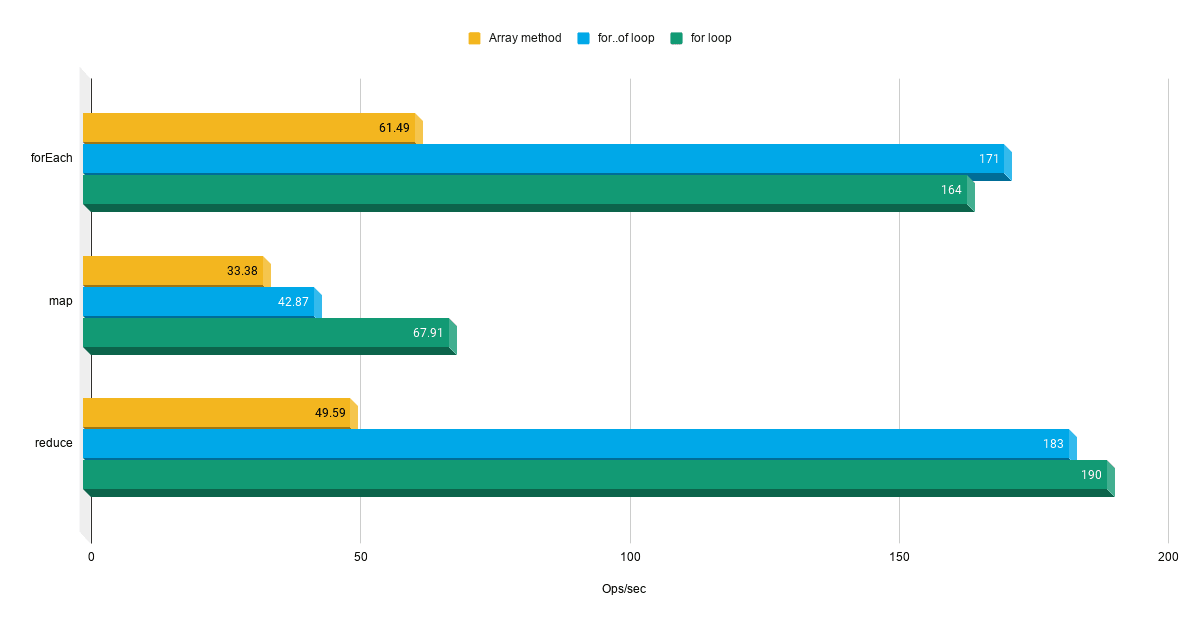


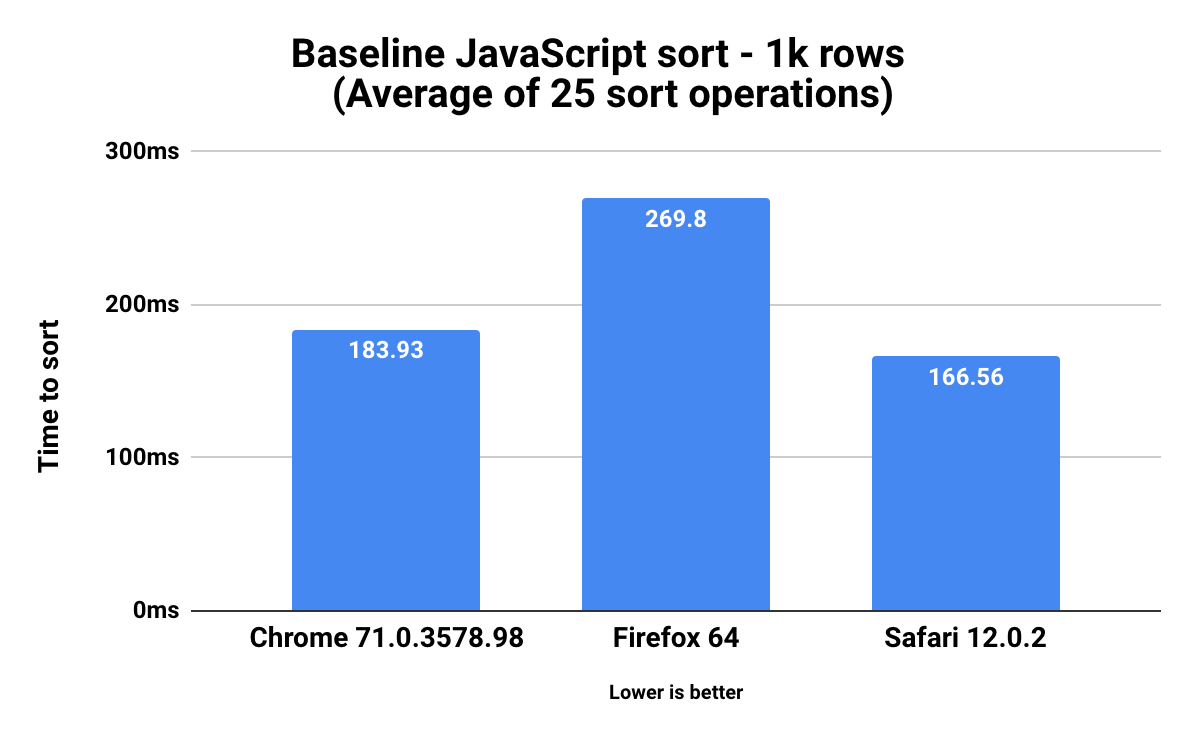
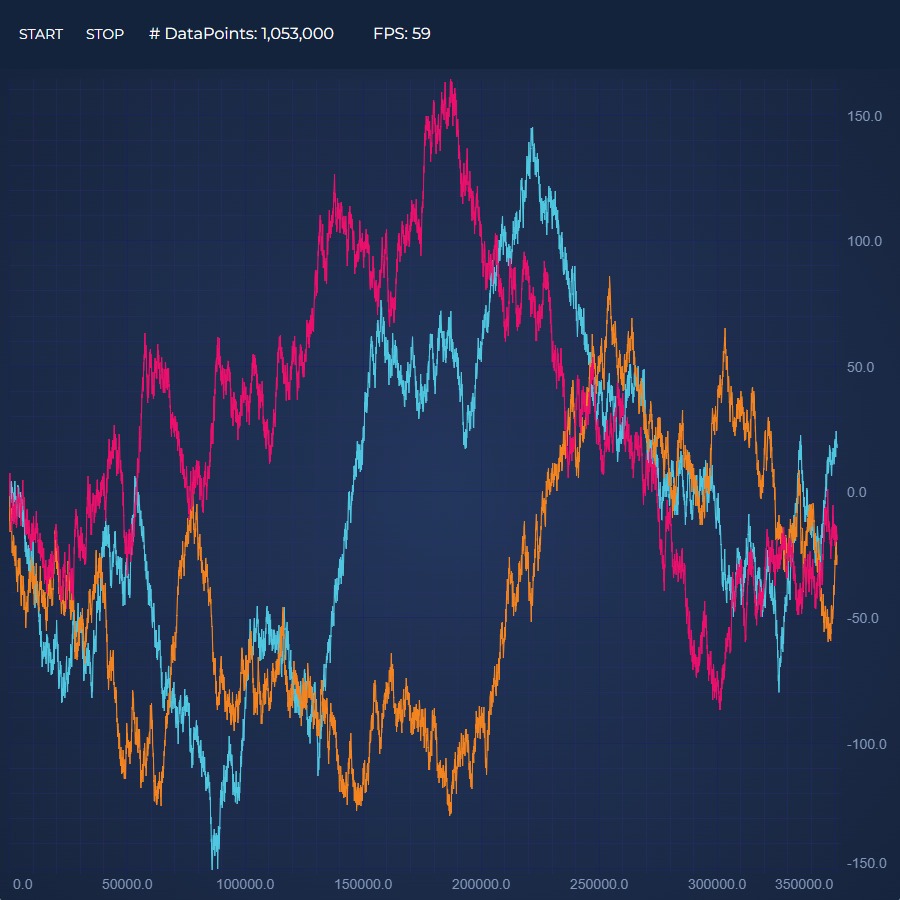



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Impact of JavaScript Size on Web Mapping Performance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Unraveling The Mystery: Exploring The Bermuda Triangle Through Google Maps
- The Intricate Web Of Territory: Exploring The Map Of The Warrior Cats
- Navigating The Landscape Of Gaming: A Comprehensive Guide To Casinos In New York State
- Unraveling The Secrets Of The Barren River Lake: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Ever-Evolving Landscape Of 2b2t: A Look At The 2021 Map
- Navigating The Terrain Of Conflict: Understanding The Map Of Vietnam During The War
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Fresno: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Geographic Landscape
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Medieval Spain: A Journey Through Maps
Leave a Reply