The Rise Of An Empire: A Geographical Examination Of Rome’s Expansion
The Rise of an Empire: A Geographical Examination of Rome’s Expansion
Related Articles: The Rise of an Empire: A Geographical Examination of Rome’s Expansion
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Rise of an Empire: A Geographical Examination of Rome’s Expansion. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Rise of an Empire: A Geographical Examination of Rome’s Expansion

The Roman Empire, a colossal entity that dominated much of the Mediterranean world for centuries, was not built overnight. Its rise to power was a gradual process, intricately woven with military conquest, political maneuvering, and strategic expansion. This expansion, however, was not merely a brute force endeavor; it was a calculated and deliberate process driven by a complex interplay of factors, including economic necessity, political ambition, and the desire for security.
To understand the full scope of Rome’s influence, it is crucial to examine its geographical expansion, a journey that transformed a small city-state into a vast empire spanning three continents. This exploration delves into the key phases of Roman expansion, highlighting the motivations behind each conquest and the lasting impact these territories had on the Roman world.
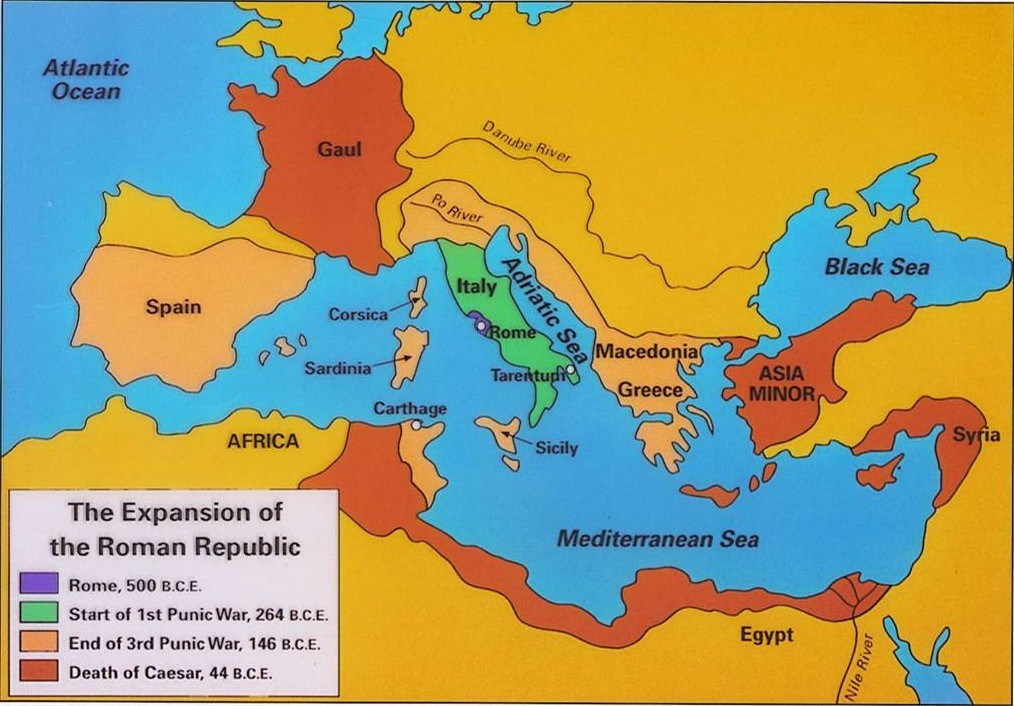
The Early Republic: Foundations of Expansion (753 BCE – 264 BCE)
The early Roman Republic, founded in 753 BCE, was initially confined to the city of Rome and its surrounding territories in Latium. This period saw the consolidation of Roman power within the Italian peninsula, a process marked by a series of wars against neighboring tribes and city-states. The Romans, with their disciplined legions and shrewd political acumen, gradually subdued their rivals, expanding their territory and establishing their authority.
The Roman conquest of the Italian peninsula was driven by several factors. Firstly, the desire for fertile agricultural land and resources was a key motivator. The Romans, with their growing population, needed access to more land to support their burgeoning economy. Secondly, the threat posed by neighboring tribes and city-states necessitated the expansion of Roman control to ensure security and prevent incursions. Lastly, the ambition of Roman leaders to establish Rome as the dominant power in Italy fueled their expansionist endeavors.
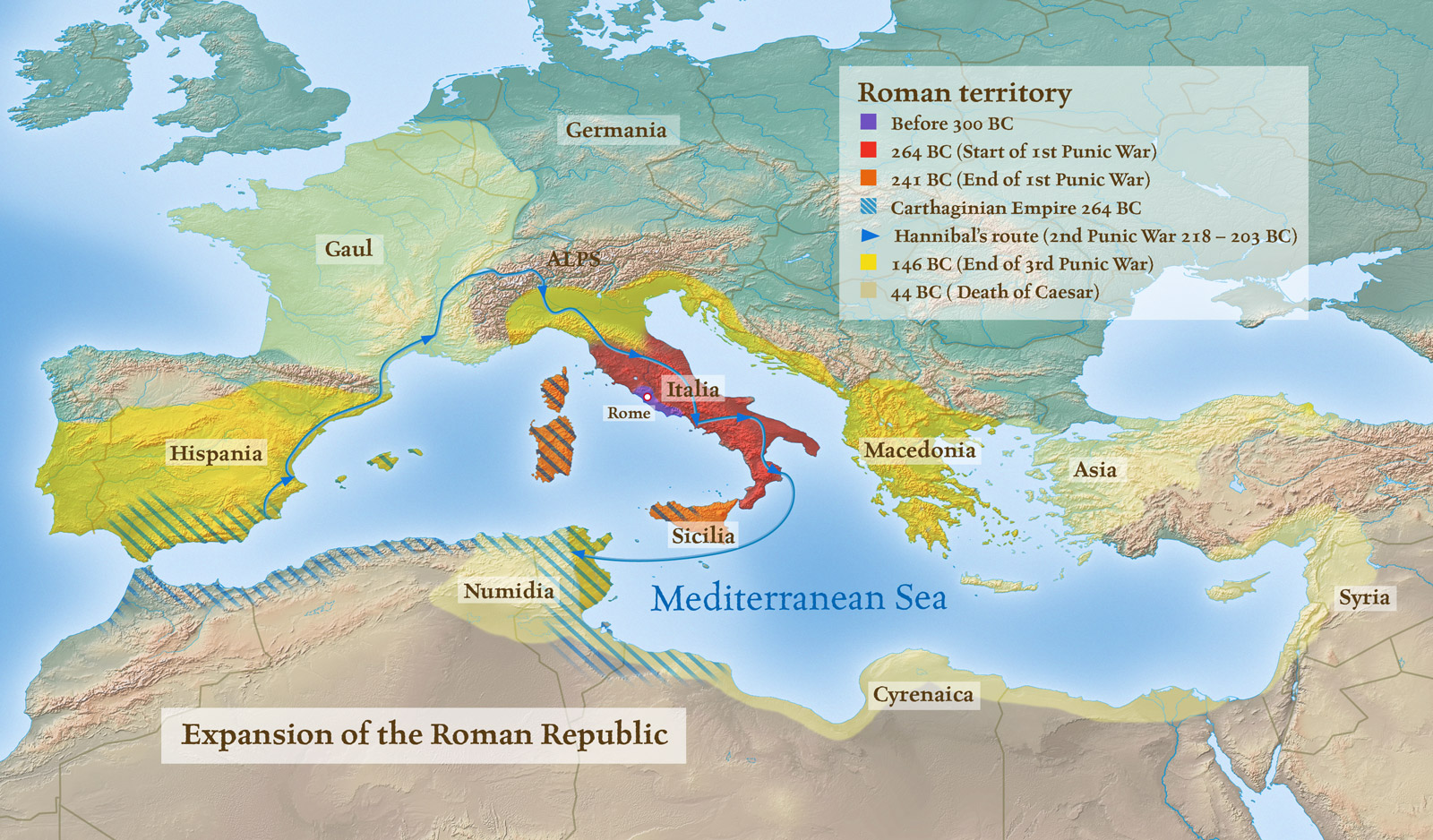
The Punic Wars: Clash of Empires (264 BCE – 146 BCE)
The clash between Rome and Carthage, a powerful Phoenician city-state in North Africa, marked a pivotal turning point in Roman history. The Punic Wars, a series of three devastating conflicts spanning over a century, saw Rome emerge as the dominant power in the Mediterranean. The first Punic War (264-241 BCE) centered around the control of Sicily, a strategically important island rich in resources. This conflict saw the Romans develop their naval capabilities, eventually defeating the Carthaginians and gaining control of Sicily.
The second Punic War (218-201 BCE) saw Hannibal, a brilliant Carthaginian general, launch a surprise attack on the Italian peninsula. Despite initial setbacks, the Romans, under the leadership of Scipio Africanus, eventually defeated Hannibal and secured their dominance over Carthage. The third Punic War (149-146 BCE) witnessed the complete destruction of Carthage, solidifying Rome’s position as the undisputed maritime power in the Mediterranean.
Expansion into the Eastern Mediterranean: The Hellenistic World (146 BCE – 30 BCE)
Following the Punic Wars, Rome began to expand eastward, encountering the Hellenistic world – a region marked by the spread of Greek culture and influence. This period saw Rome conquer Macedonia, Greece, and the kingdoms of Pergamum and Bithynia, bringing these territories under Roman control. The Romans were drawn to the Hellenistic world by its wealth, strategic location, and the allure of Greek culture.
The conquest of Greece in 146 BCE marked a significant turning point, as it brought Rome into direct contact with the intellectual and artistic legacy of ancient Greece. This encounter had a profound impact on Roman society, leading to the adoption of Greek art, literature, philosophy, and political institutions.
The Roman Republic: A Period of Consolidation and Growth (146 BCE – 31 BCE)
The period following the conquest of Greece saw Rome solidify its control over its vast empire, establishing a complex system of governance and administration. This period witnessed the rise of Roman provinces, each governed by a Roman governor appointed by the Senate. The Romans implemented a system of taxation, infrastructure development, and military garrisons to maintain order and stability throughout their vast empire.
This period also saw the rise of ambitious Roman generals, such as Julius Caesar, who sought to expand Roman power further. Caesar’s conquest of Gaul (present-day France) brought vast territories and resources under Roman control. His subsequent invasion of Egypt and his assassination in 44 BCE marked the beginning of the end for the Roman Republic.
The Roman Empire: Pax Romana (31 BCE – 284 CE)
The assassination of Julius Caesar plunged Rome into a period of civil war, ultimately leading to the rise of Augustus Caesar, the first Roman emperor. Augustus established the Roman Empire, ushering in an era of peace and prosperity known as the Pax Romana. This period saw the expansion of Roman power into new territories, including the conquest of Egypt, Judea, and Armenia.
The Roman Empire under Augustus and his successors saw the construction of a vast network of roads, aqueducts, and public buildings, fostering trade and cultural exchange throughout the empire. The Pax Romana, however, was not a period of perpetual peace. The empire faced numerous challenges, including rebellions, invasions, and economic instability.
The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire (284 CE – 476 CE)
The 3rd century CE saw the Roman Empire face a series of crises, including economic depression, military instability, and political turmoil. The empire was plagued by internal strife, barbarian invasions, and the rise of new religious movements, culminating in the division of the empire into East and West in 395 CE.
The Western Roman Empire eventually collapsed in 476 CE, marking the end of Roman rule in the west. However, the Eastern Roman Empire, also known as the Byzantine Empire, continued to flourish for another thousand years, preserving the legacy of Roman civilization in the East.
The Legacy of Roman Expansion
The expansion of the Roman Empire had a profound and lasting impact on the course of history. The Romans brought with them their system of law, administration, and infrastructure, leaving an indelible mark on the civilizations they encountered. Roman roads, aqueducts, and public buildings stand as testaments to their engineering prowess and their commitment to public works.
The Roman legal system, with its emphasis on fairness and justice, served as a model for legal systems throughout Europe and beyond. Roman literature, art, and philosophy influenced the development of Western culture for centuries. The spread of Christianity, which originated in Judea, was facilitated by the Pax Romana, eventually becoming the dominant religion of the Western world.
FAQs
1. What were the main motivations behind Roman expansion?
The Romans were driven by a combination of factors, including economic necessity, political ambition, and the desire for security. They sought fertile land, resources, and strategic locations to secure their borders and maintain their dominance.
2. How did Roman expansion impact the societies they conquered?
Roman expansion had a profound impact on the societies they conquered. The Romans introduced their language, laws, and culture, often leading to the assimilation of conquered peoples into Roman society. However, Roman expansion also brought about significant changes, including the displacement of populations, the destruction of local cultures, and the exploitation of conquered territories.
3. What were the benefits of Roman expansion?
Roman expansion brought about a period of peace and prosperity known as the Pax Romana, which facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of knowledge throughout the empire. The Romans also developed a vast infrastructure, including roads, aqueducts, and public buildings, that benefited the entire empire.
4. What were the drawbacks of Roman expansion?
Roman expansion also had its drawbacks. It led to the exploitation of conquered territories, the displacement of populations, and the destruction of local cultures. It also contributed to the eventual decline of the Roman Empire, as it became increasingly difficult to maintain control over such a vast territory.
5. What are the lasting legacies of Roman expansion?
Roman expansion left a lasting legacy on the world, including the spread of Roman law, language, and culture. The Romans also developed a system of administration and infrastructure that influenced the development of Western civilization.
Tips for Studying Roman Expansion
- Focus on key events and figures: Studying the major battles, political figures, and key turning points in Roman history can help you gain a better understanding of the process of expansion.
- Explore primary sources: Examining Roman texts, such as historical accounts, letters, and speeches, can provide valuable insights into the motivations and perspectives of the Romans themselves.
- Consider the impact on conquered societies: It is important to consider the impact of Roman expansion on the societies they conquered, not just the benefits for the Romans themselves.
- Use maps and visual aids: Maps and visual aids can help you visualize the geographical scope of Roman expansion and its impact on different regions.
- Connect Roman expansion to broader historical themes: Roman expansion can be understood in the context of broader historical themes, such as the rise and fall of empires, the spread of civilizations, and the interaction of cultures.
Conclusion
The expansion of the Roman Empire was a complex and multifaceted process driven by a combination of factors. It was a journey marked by both conquest and assimilation, leaving a lasting impact on the course of history. The Romans, through their military prowess, political acumen, and cultural influence, transformed a small city-state into a vast empire that dominated much of the Mediterranean world for centuries. Their legacy, in the form of law, language, infrastructure, and cultural influence, continues to resonate in the modern world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Rise of an Empire: A Geographical Examination of Rome’s Expansion. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Unraveling The Mystery: Exploring The Bermuda Triangle Through Google Maps
- The Intricate Web Of Territory: Exploring The Map Of The Warrior Cats
- Navigating The Landscape Of Gaming: A Comprehensive Guide To Casinos In New York State
- Unraveling The Secrets Of The Barren River Lake: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Ever-Evolving Landscape Of 2b2t: A Look At The 2021 Map
- Navigating The Terrain Of Conflict: Understanding The Map Of Vietnam During The War
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Fresno: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Geographic Landscape
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Medieval Spain: A Journey Through Maps
Leave a Reply