Uncovering The Riches Beneath: A Comprehensive Guide To The United States Natural Resources Map
Uncovering the Riches Beneath: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Natural Resources Map
Related Articles: Uncovering the Riches Beneath: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Natural Resources Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Uncovering the Riches Beneath: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Natural Resources Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Uncovering the Riches Beneath: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Natural Resources Map
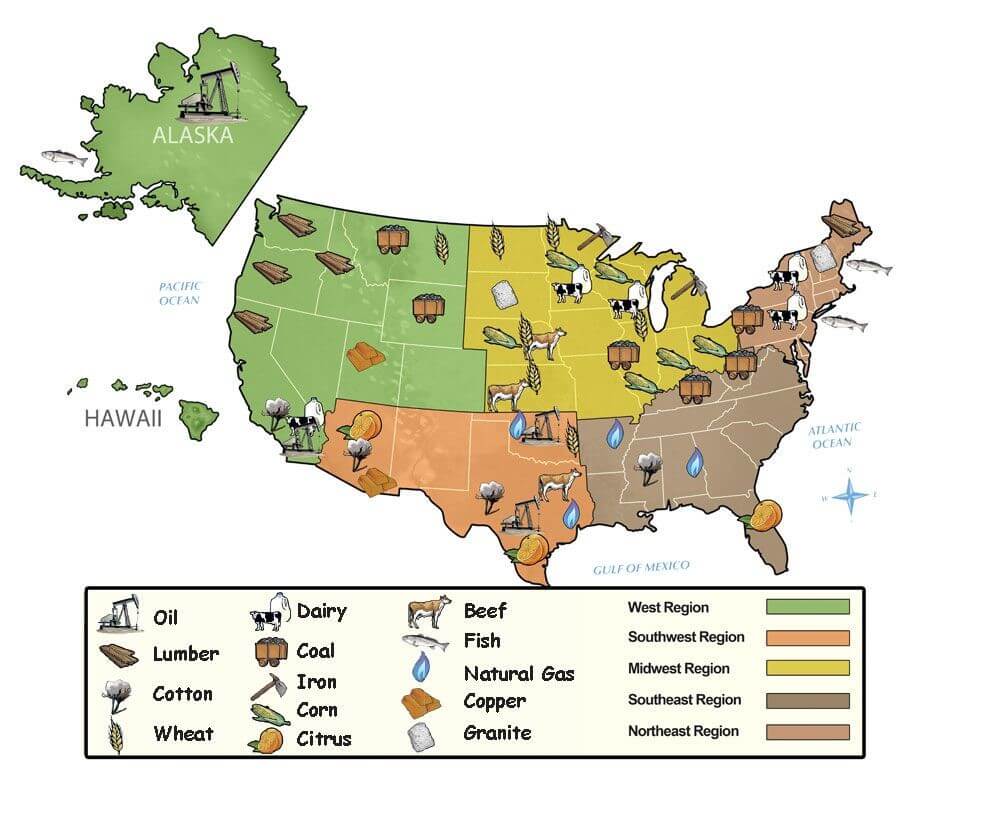
The United States, a vast and diverse nation, boasts a remarkable array of natural resources. From the fertile farmlands of the Midwest to the towering forests of the Pacific Northwest, the country’s landscape holds an abundance of raw materials that have fueled its growth and prosperity. Understanding the distribution and significance of these resources is crucial for informed decision-making in various sectors, including energy, agriculture, manufacturing, and environmental conservation.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate tapestry of the United States natural resources map, offering a detailed examination of key resources and their geographical distribution. We will explore the economic and environmental implications of resource availability, the challenges posed by resource depletion, and the strategies employed for sustainable management.
A Diverse Landscape, A Wealth of Resources:
The United States natural resources map is a vibrant mosaic reflecting the country’s diverse geological formations and climatic conditions. This diversity translates into a wealth of resources, categorized broadly as follows:
1. Energy Resources:
- Fossil Fuels: The United States remains a major producer of fossil fuels, with significant reserves of coal, oil, and natural gas. Coal reserves are concentrated in the Appalachian region, the Powder River Basin, and the Illinois Basin. Oil and natural gas production is prevalent in Texas, North Dakota, and the Gulf of Mexico.
- Renewable Energy: The country has made strides in developing renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, geothermal, and hydroelectric power. Solar energy potential is highest in the Southwest, while wind energy resources are abundant in the Great Plains and along the coasts. Geothermal energy is concentrated in the West, particularly in California and Nevada. Hydroelectric power is primarily generated in the Pacific Northwest and the Southeast.
2. Mineral Resources:
- Metallic Minerals: The United States is rich in metallic minerals, including copper, iron ore, gold, silver, and aluminum. Copper deposits are found in Arizona, Utah, and Montana. Iron ore is primarily mined in Minnesota and Michigan. Gold and silver production is concentrated in Nevada, Alaska, and California. Aluminum is extracted from bauxite, a major source of which is found in Arkansas.
- Non-Metallic Minerals: The country also possesses significant reserves of non-metallic minerals, such as limestone, granite, sand, gravel, and phosphate rock. Limestone is used in construction and manufacturing, while granite is a popular building material. Sand and gravel are essential for construction projects, and phosphate rock is crucial for fertilizer production.
3. Agricultural Resources:
- Croplands: The United States is a global leader in agricultural production, with vast expanses of fertile croplands. The Midwest, known as the "breadbasket of America," is renowned for its corn, soybean, and wheat production. Other major agricultural regions include the Great Plains, the Delta region, and California.
- Forests: The country’s forests are a vital resource, providing timber, pulpwood, and a wide range of ecosystem services. The Pacific Northwest, the Southeast, and the Northeast are home to extensive forestlands.
4. Water Resources:
- Surface Water: The United States has an abundance of surface water resources, including rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. The Mississippi River system, the largest in the country, plays a crucial role in transportation, agriculture, and recreation. The Great Lakes region holds a significant portion of the world’s freshwater.
- Groundwater: Groundwater is a critical source of water for many communities, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. The Ogallala Aquifer, located in the Great Plains, is the largest underground aquifer in the United States.
The Economic and Environmental Importance of Natural Resources:
The United States natural resources map is not merely a geographical depiction; it is a reflection of the country’s economic engine and environmental well-being.
Economic Significance:
- Job Creation: Natural resource extraction and processing industries are major employers across the country, generating jobs in mining, logging, agriculture, energy production, and manufacturing.
- Economic Growth: The exploitation of natural resources has played a pivotal role in the economic growth of the United States, contributing to its industrialization and technological advancement.
- International Trade: The United States is a significant exporter of natural resources, including agricultural products, energy, and minerals, contributing to its global trade balance.
Environmental Significance:
- Ecosystem Services: Natural resources provide essential ecosystem services, such as clean air and water, soil fertility, and biodiversity. Forests, wetlands, and grasslands play a critical role in regulating climate, filtering pollutants, and supporting wildlife habitats.
- Conservation: The sustainable management of natural resources is crucial for protecting the environment, ensuring the availability of resources for future generations, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the United States enjoys a wealth of natural resources, several challenges and opportunities exist in their management and utilization.
Challenges:
- Resource Depletion: The extraction and consumption of finite resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals, raise concerns about resource depletion and the need for sustainable alternatives.
- Environmental Impacts: The extraction and processing of natural resources can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat loss, pollution, and climate change.
- Resource Conflicts: Conflicts over resource allocation can arise between different stakeholders, including communities, industries, and governments.
Opportunities:
- Technological Innovation: Advances in technology are enabling the development of new resource extraction methods, renewable energy technologies, and resource conservation strategies.
- Sustainable Practices: The adoption of sustainable practices in resource management, such as recycling, conservation, and renewable energy, can help mitigate environmental impacts and ensure resource availability for future generations.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation is essential for addressing global resource challenges, such as climate change and biodiversity loss.
FAQs About the United States Natural Resources Map:
1. What are the most important natural resources in the United States?
The most important natural resources in the United States include fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas), metallic minerals (copper, iron ore, gold, silver), agricultural products (corn, soybeans, wheat), timber, and water.
2. Where are the major energy resources located in the United States?
Coal reserves are concentrated in the Appalachian region, the Powder River Basin, and the Illinois Basin. Oil and natural gas production is prevalent in Texas, North Dakota, and the Gulf of Mexico. Renewable energy resources, such as solar, wind, geothermal, and hydroelectric power, are distributed throughout the country, with specific concentrations in the Southwest, Great Plains, West, and Pacific Northwest.
3. What are the environmental impacts of natural resource extraction?
Natural resource extraction can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat loss, pollution, deforestation, and climate change. Mining operations can release pollutants into the air, water, and soil. Logging can lead to deforestation and habitat loss. Fossil fuel extraction and combustion contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, driving climate change.
4. How is the United States working to address resource depletion?
The United States is working to address resource depletion through a combination of strategies, including:
- Conservation: Promoting resource conservation measures, such as reducing energy consumption, recycling, and using water efficiently.
- Renewable Energy: Investing in renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, geothermal, and hydropower, to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Resource Recovery: Developing technologies for recovering resources from waste materials, such as recycling and composting.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating with other countries to address global resource challenges, such as climate change and resource depletion.
Tips for Understanding the United States Natural Resources Map:
- Visualize the Data: Utilize maps, charts, and graphs to visualize the distribution of natural resources across the country.
- Explore Different Scales: Analyze resource distribution at different scales, from local to regional to national levels.
- Consider Interconnections: Recognize the interconnectedness of natural resources and the impact of resource extraction on other environmental systems.
- Stay Informed: Follow developments in resource management, technology, and policy to stay informed about current challenges and opportunities.
Conclusion:
The United States natural resources map is a testament to the country’s vast and diverse landscape. From energy resources to minerals, agricultural products, forests, and water, the nation possesses a wealth of raw materials that have played a pivotal role in its economic growth and prosperity. However, the sustainable management of these resources is crucial for ensuring their availability for future generations and mitigating the environmental impacts of resource extraction. By embracing innovation, implementing sustainable practices, and fostering international cooperation, the United States can continue to harness its natural resources while safeguarding the environment for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Uncovering the Riches Beneath: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Natural Resources Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Unraveling The Mystery: Exploring The Bermuda Triangle Through Google Maps
- The Intricate Web Of Territory: Exploring The Map Of The Warrior Cats
- Navigating The Landscape Of Gaming: A Comprehensive Guide To Casinos In New York State
- Unraveling The Secrets Of The Barren River Lake: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Ever-Evolving Landscape Of 2b2t: A Look At The 2021 Map
- Navigating The Terrain Of Conflict: Understanding The Map Of Vietnam During The War
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Fresno: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Geographic Landscape
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Medieval Spain: A Journey Through Maps
Leave a Reply