Understanding The Complex Tapestry: A Detailed Examination Of Yugoslavia’s Ethnic Map
Understanding the Complex Tapestry: A Detailed Examination of Yugoslavia’s Ethnic Map
Related Articles: Understanding the Complex Tapestry: A Detailed Examination of Yugoslavia’s Ethnic Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Complex Tapestry: A Detailed Examination of Yugoslavia’s Ethnic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Complex Tapestry: A Detailed Examination of Yugoslavia’s Ethnic Map
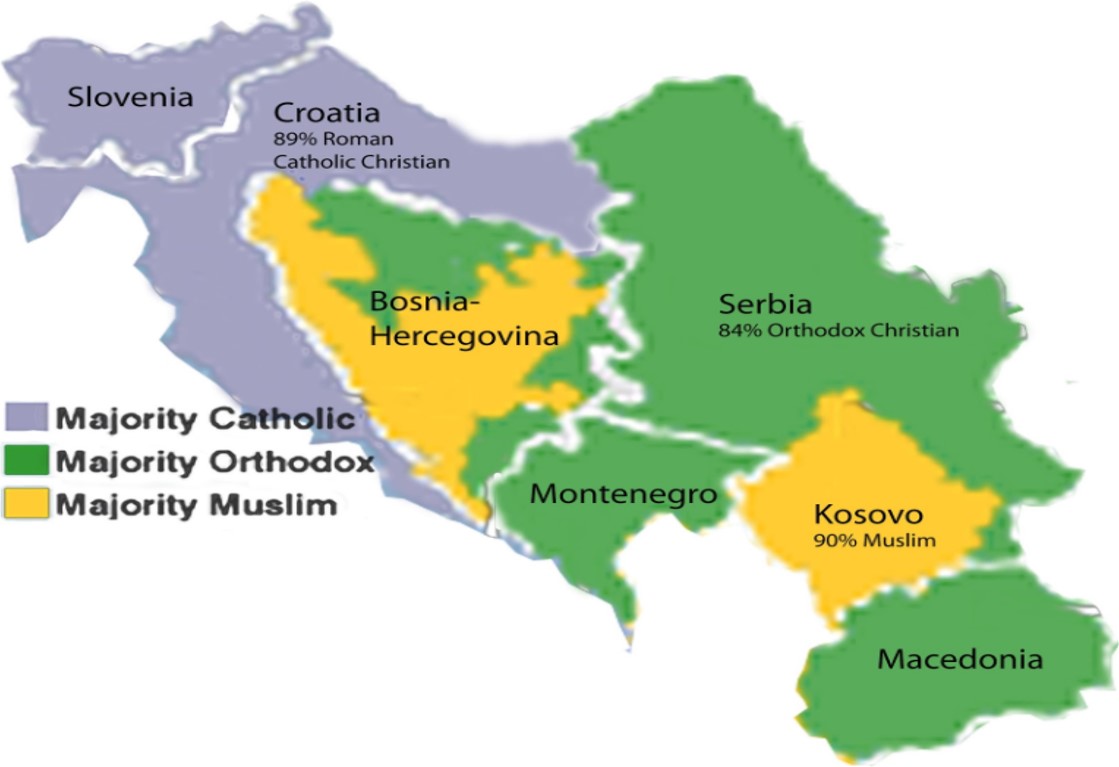
The former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, a nation forged from the ashes of World War I, was a fascinating example of a multi-ethnic state. Its diverse population, composed of six constituent republics, each with its unique cultural and linguistic identity, presented a complex picture of ethnic distribution. This article delves into the intricate mosaic of Yugoslavia’s ethnic map, analyzing its formation, evolution, and the factors that contributed to its eventual dissolution.
The Mosaic of Identities: A Historical Perspective
Yugoslavia’s ethnic map was shaped by a confluence of historical, geographical, and political factors. The region, situated at the crossroads of Europe and the Balkans, has witnessed centuries of migrations, conquests, and cultural exchanges. The Ottoman Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and various Slavic kingdoms left their imprints on the region’s ethnic landscape.
- Serbs: The largest ethnic group in Yugoslavia, Serbs were primarily concentrated in Serbia, Montenegro, and parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Their historical roots can be traced back to the medieval Serbian Empire, which played a significant role in defending the Balkans from Ottoman expansion.
- Croats: Primarily residing in Croatia, Croats shared a similar Slavic heritage with Serbs. Their cultural and linguistic distinctions stemmed from historical alliances with the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Catholic Church.
- Bosniaks: The majority population of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosniaks were primarily Muslim Slavs. Their history was intertwined with the Ottoman Empire, which had a lasting impact on their culture and religion.
- Slovenes: Occupying the northwestern corner of Yugoslavia, Slovenes were the smallest of the six constituent republics. Their distinct cultural identity was shaped by their proximity to Austria and their historical ties to the Habsburg Empire.
- Macedonians: Primarily inhabiting the Republic of Macedonia, Macedonians were a distinct Slavic group with a rich cultural heritage. Their history was marked by periods of Ottoman rule and subsequent attempts to establish their own national identity.
- Montenegrins: Predominantly residing in Montenegro, Montenegrins shared a close cultural and linguistic kinship with Serbs. Their history was marked by periods of independence and periods of integration with Serbia.
The Shifting Sands of Ethnicity: Post-World War II
The aftermath of World War II witnessed significant changes in Yugoslavia’s ethnic landscape. The establishment of the socialist state led to policies promoting inter-ethnic harmony and national unity. While the official ideology emphasized a unified Yugoslav identity, the diverse cultural and linguistic identities of the constituent republics continued to persist.
- Migration and Resettlement: The post-war period saw significant population movements within Yugoslavia, particularly from rural areas to urban centers. This internal migration contributed to the intermingling of different ethnic groups in various regions of the country.
- National Identity and Autonomy: The Yugoslav government, while promoting a unified national identity, also granted a degree of autonomy to the constituent republics. This allowed for the preservation of distinct cultural traditions and languages.
- Ethnic Tensions and Nationalism: Despite the official emphasis on unity, underlying ethnic tensions continued to simmer beneath the surface. These tensions were often fueled by historical grievances, competing national narratives, and economic disparities.
The Unraveling of Unity: The 1990s and the Breakup of Yugoslavia
The 1990s witnessed the disintegration of Yugoslavia, a process fueled by the resurgence of nationalism and ethnic tensions. The collapse of the communist system in Eastern Europe and the rise of democratic movements in the region provided fertile ground for nationalist sentiments to take root.
- The Rise of Nationalism: The decline of the communist system in Yugoslavia led to a resurgence of nationalist movements in each of the constituent republics. These movements sought to assert their distinct identities and autonomy, often at the expense of inter-ethnic harmony.
- The Yugoslav Wars: The escalating ethnic tensions culminated in a series of bloody conflicts in the early 1990s. The wars in Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Kosovo resulted in widespread human suffering, displacement, and ethnic cleansing.
- The Legacy of Division: The breakup of Yugoslavia left a lasting legacy of division and mistrust among its former constituent republics. The ethnic conflicts of the 1990s continue to cast a long shadow on the region, with unresolved issues and lingering tensions persisting even today.
The Significance of Understanding Yugoslavia’s Ethnic Map
Understanding the complex ethnic map of Yugoslavia is crucial for comprehending the historical, political, and social dynamics that shaped the region. This knowledge provides valuable insights into:
- The Roots of Conflict: Analyzing the ethnic distribution and historical grievances can shed light on the underlying causes of the Yugoslav wars and the ongoing tensions in the region.
- The Challenges of Nation-Building: The experience of Yugoslavia serves as a cautionary tale about the challenges of building a unified nation-state from diverse ethnic groups.
- The Importance of Inter-Ethnic Harmony: Understanding the complexities of ethnic relations is essential for fostering inter-ethnic dialogue, reconciliation, and cooperation in the region.
FAQs
Q: What were the main ethnic groups in Yugoslavia?
A: The main ethnic groups in Yugoslavia were Serbs, Croats, Bosniaks, Slovenes, Macedonians, and Montenegrins.
Q: How did Yugoslavia’s ethnic map change over time?
A: Yugoslavia’s ethnic map was influenced by historical migrations, conquests, and political changes. Post-World War II policies aimed at promoting inter-ethnic harmony, but underlying tensions and the rise of nationalism ultimately led to its disintegration.
Q: What role did nationalism play in the breakup of Yugoslavia?
A: Nationalism played a significant role in the breakup of Yugoslavia. The rise of nationalist movements in each of the constituent republics fueled tensions and ultimately led to the outbreak of war.
Q: What are the lasting consequences of the Yugoslav wars?
A: The Yugoslav wars left a lasting legacy of division and mistrust among the former constituent republics. The conflicts resulted in widespread human suffering, displacement, and ethnic cleansing, and unresolved issues and lingering tensions persist even today.
Tips
- Engage with historical sources: Studying historical accounts, maps, and documents can provide valuable insights into the formation and evolution of Yugoslavia’s ethnic map.
- Explore the cultural diversity: Researching the unique cultural traditions, languages, and histories of the different ethnic groups can deepen your understanding of the region’s complexity.
- Be aware of the challenges: Recognizing the complexities of ethnic relations and the challenges of building inter-ethnic harmony is essential for navigating the region’s history and present-day realities.
Conclusion
Yugoslavia’s ethnic map was a tapestry woven with threads of history, culture, and politics. Its complexity and dynamism ultimately led to its dissolution, leaving behind a legacy of conflict, division, and unresolved issues. Understanding the intricate mosaic of ethnic identities within the former Yugoslav state is crucial for comprehending the region’s past, present, and future. By acknowledging the complexities of ethnic relations and embracing the principles of inter-ethnic harmony, the countries of the former Yugoslavia can strive towards a more peaceful and prosperous future.

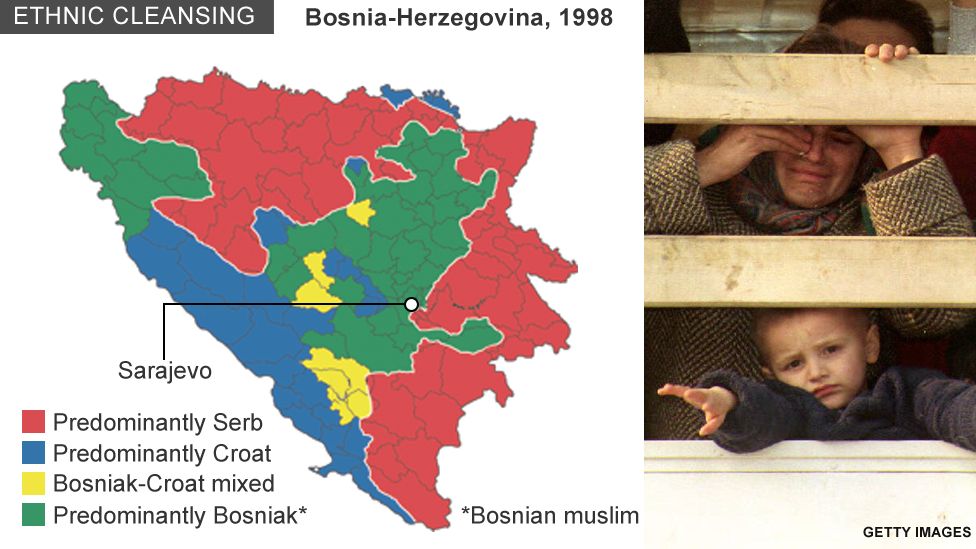





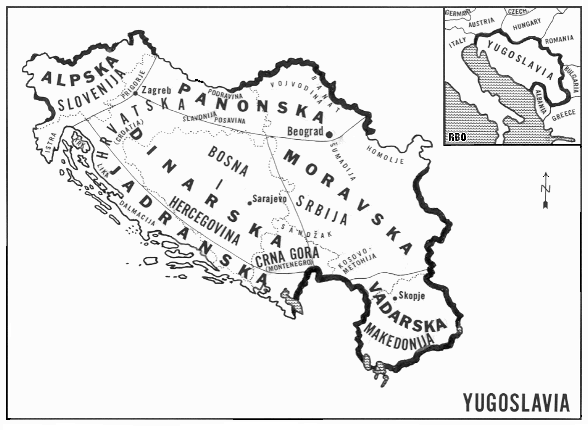
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Complex Tapestry: A Detailed Examination of Yugoslavia’s Ethnic Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Unraveling The Mystery: Exploring The Bermuda Triangle Through Google Maps
- The Intricate Web Of Territory: Exploring The Map Of The Warrior Cats
- Navigating The Landscape Of Gaming: A Comprehensive Guide To Casinos In New York State
- Unraveling The Secrets Of The Barren River Lake: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Ever-Evolving Landscape Of 2b2t: A Look At The 2021 Map
- Navigating The Terrain Of Conflict: Understanding The Map Of Vietnam During The War
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Fresno: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Geographic Landscape
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Medieval Spain: A Journey Through Maps
Leave a Reply