Unraveling The Grid Of The Earth: A Comprehensive Guide To Meridian Lines
Unraveling the Grid of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Meridian Lines
Related Articles: Unraveling the Grid of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Meridian Lines
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Grid of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Meridian Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Grid of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Meridian Lines
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Grid of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Meridian Lines
- 3.1 Defining the Meridian Lines: A Fundamental Framework
- 3.2 The Prime Meridian: A Global Reference Point
- 3.3 The Importance of Meridian Lines: A Foundation for Navigation and Mapping
- 3.4 Applications of Meridian Lines: Beyond Geography
- 3.5 The Evolution of Meridian Lines: A Journey Through History
- 3.6 Meridian Lines: A Global Network with a Local Impact
- 3.7 FAQs about Meridian Lines
- 3.8 Tips for Understanding Meridian Lines
- 3.9 Conclusion: A Timeless Framework
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Grid of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Meridian Lines

The Earth, in its vastness and complexity, is often visualized as a sphere suspended in space. But beneath the surface of continents and oceans lies a hidden network of lines that define its very essence. These lines, known as meridians, are invisible but fundamental, forming the backbone of our understanding of global geography and navigation. This article delves into the fascinating world of meridian lines, exploring their definition, significance, and practical applications.
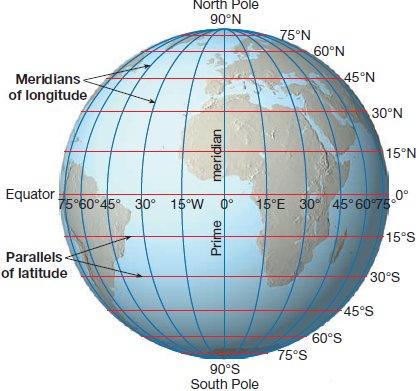
Defining the Meridian Lines: A Fundamental Framework
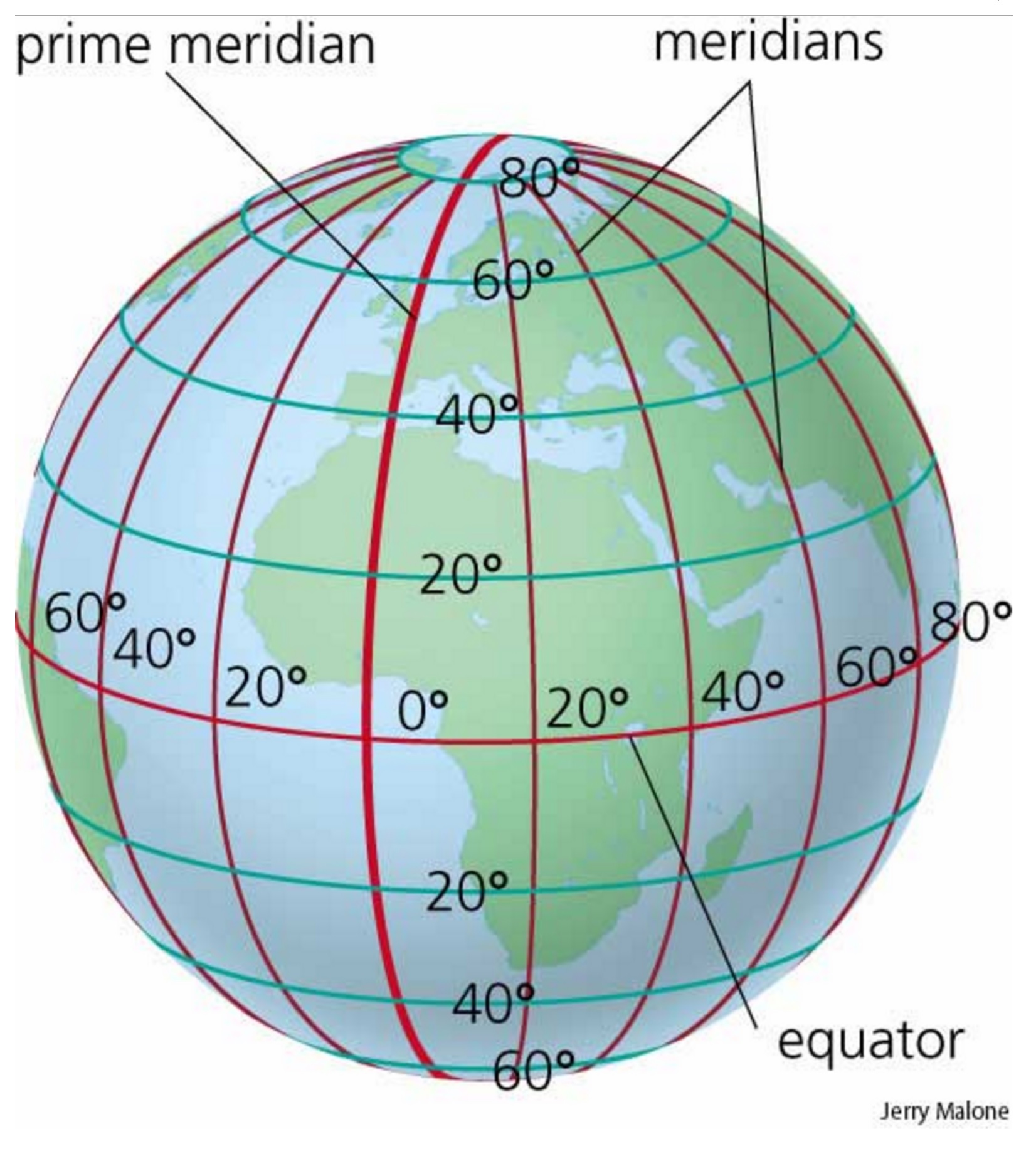
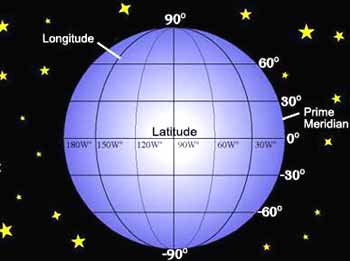
Meridian lines, also referred to as lines of longitude, are imaginary circles that run from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting the equator at right angles. They are fundamental to our understanding of Earth’s geography, serving as a crucial element in the global coordinate system. Each meridian line represents a specific longitude, measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian, which is the zero-degree meridian passing through Greenwich, England.
The Prime Meridian: A Global Reference Point
The prime meridian, also known as the Greenwich meridian, serves as the zero-degree reference point for all other meridians. Its significance lies in its role as a universal standard for measuring longitude. This line, passing through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
The Importance of Meridian Lines: A Foundation for Navigation and Mapping
Meridian lines are crucial for navigation, cartography, and understanding the Earth’s geographical features. They provide a consistent and reliable system for locating any point on the planet. Here’s how they contribute:
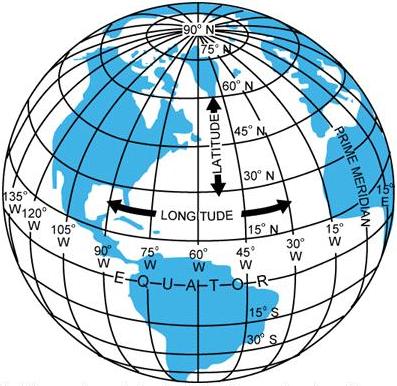
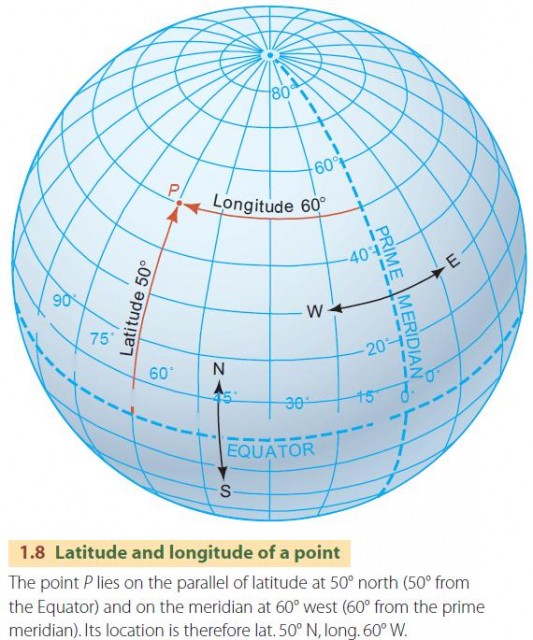
- Precise Location: Meridian lines, in conjunction with latitude lines (circles parallel to the equator), form the foundation of the global coordinate system. This system allows for the precise determination of any point on Earth using its latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Navigation: Sailors, pilots, and explorers rely on meridian lines to navigate across vast distances. By knowing their current longitude, they can determine their position relative to specific landmarks and destinations.
- Mapping: Meridian lines are essential for creating accurate maps of the Earth. They provide a framework for representing the planet’s surface in a two-dimensional format, preserving the relative positions of continents, countries, and other geographical features.
- Time Zones: Meridian lines play a crucial role in defining time zones. Each time zone corresponds to a 15-degree band of longitude, ensuring consistent timekeeping across different regions of the Earth.
Applications of Meridian Lines: Beyond Geography
Meridian lines extend beyond their geographical applications, influencing various aspects of our lives:
- Satellite Communication: Meridian lines are used in satellite communication systems to determine the position of satellites and ensure reliable transmission of signals.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use meridian lines to track the movement of celestial objects and determine their position in the sky.
- Geodesy: Geodesists rely on meridian lines to study the Earth’s shape and gravitational field, contributing to our understanding of Earth’s dynamic processes.
The Evolution of Meridian Lines: A Journey Through History
The concept of meridian lines has evolved over centuries, driven by advancements in navigation, cartography, and scientific understanding. Here’s a glimpse into its historical journey:
- Ancient Civilizations: Early civilizations, including the Egyptians and Greeks, recognized the importance of celestial observations for navigation and timekeeping. They developed rudimentary systems for dividing the Earth into zones, foreshadowing the concept of meridian lines.
- The Age of Exploration: The era of exploration, marked by voyages across oceans, spurred the development of more sophisticated navigational techniques. This led to the creation of accurate maps and the establishment of the prime meridian at Greenwich, England.
- The Scientific Revolution: Scientific advancements during the 17th and 18th centuries, including the invention of the telescope and the development of calculus, revolutionized our understanding of the Earth’s shape and motion. These advancements paved the way for a more precise definition of meridian lines and their role in global mapping.
- Modern Era: In the 20th and 21st centuries, technological advancements, including satellite navigation systems (GPS) and digital mapping software, have further refined our understanding and utilization of meridian lines.
Meridian Lines: A Global Network with a Local Impact
While meridian lines are imaginary, their impact is tangible and far-reaching. They influence our understanding of the world, guide our navigation, and shape our perception of time. Their significance extends beyond the realm of geography, playing a vital role in various fields, from communication and astronomy to geodesy and satellite technology.
FAQs about Meridian Lines
Q: Why is the prime meridian located at Greenwich, England?
A: The prime meridian’s location at Greenwich, England, was established by international agreement in the late 19th century. This choice was influenced by the prominence of the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, which had already been a leading center for astronomical observations and navigation for centuries.
Q: How many meridian lines are there?
A: Theoretically, there are an infinite number of meridian lines, as they can be drawn at any point along the Earth’s surface. However, for practical purposes, we use a limited number of meridian lines, typically spaced at 15-degree intervals, to define time zones and create maps.
Q: How do meridian lines affect time zones?
A: Meridian lines are directly related to time zones. Each time zone corresponds to a 15-degree band of longitude, with the time in each zone being one hour ahead of the zone to its west. This system helps ensure consistent timekeeping across different regions of the Earth.
Q: Are meridian lines still relevant in the age of GPS?
A: While GPS technology has revolutionized navigation, meridian lines remain relevant. GPS relies on a network of satellites to determine location, and these satellites are positioned based on their latitude and longitude, which are defined by meridian lines.
Q: What is the difference between meridian lines and latitude lines?
A: Meridian lines run from the North Pole to the South Pole, defining longitude. Latitude lines, on the other hand, run parallel to the equator, defining latitude. Together, they form the global coordinate system, allowing us to pinpoint any location on Earth.
Tips for Understanding Meridian Lines
- Visualize the Earth: Imagine the Earth as a sphere, and visualize meridian lines as imaginary circles running from the North Pole to the South Pole. This mental image can help you understand their basic structure and function.
- Explore Interactive Maps: Utilize online mapping tools and interactive globes to explore the relationship between meridian lines, latitude lines, and geographical features. This interactive approach can enhance your understanding of the global coordinate system.
- Learn about Time Zones: Study the relationship between meridian lines and time zones. Understanding how time zones are defined based on longitude can provide valuable insights into the global system of timekeeping.
Conclusion: A Timeless Framework
Meridian lines, despite their invisible nature, are a fundamental aspect of our understanding of the Earth. They provide a framework for navigation, mapping, and timekeeping, shaping our perception of the world and guiding our interactions with it. As technology continues to evolve, the significance of meridian lines remains unwavering, serving as a timeless foundation for exploring and understanding our planet.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Grid of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Meridian Lines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Unraveling The Mystery: Exploring The Bermuda Triangle Through Google Maps
- The Intricate Web Of Territory: Exploring The Map Of The Warrior Cats
- Navigating The Landscape Of Gaming: A Comprehensive Guide To Casinos In New York State
- Unraveling The Secrets Of The Barren River Lake: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Ever-Evolving Landscape Of 2b2t: A Look At The 2021 Map
- Navigating The Terrain Of Conflict: Understanding The Map Of Vietnam During The War
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Fresno: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Geographic Landscape
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Medieval Spain: A Journey Through Maps
Leave a Reply