Unveiling The Sahel: A Geographical And Ecological Tapestry
Unveiling the Sahel: A Geographical and Ecological Tapestry
Related Articles: Unveiling the Sahel: A Geographical and Ecological Tapestry
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Sahel: A Geographical and Ecological Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Sahel: A Geographical and Ecological Tapestry

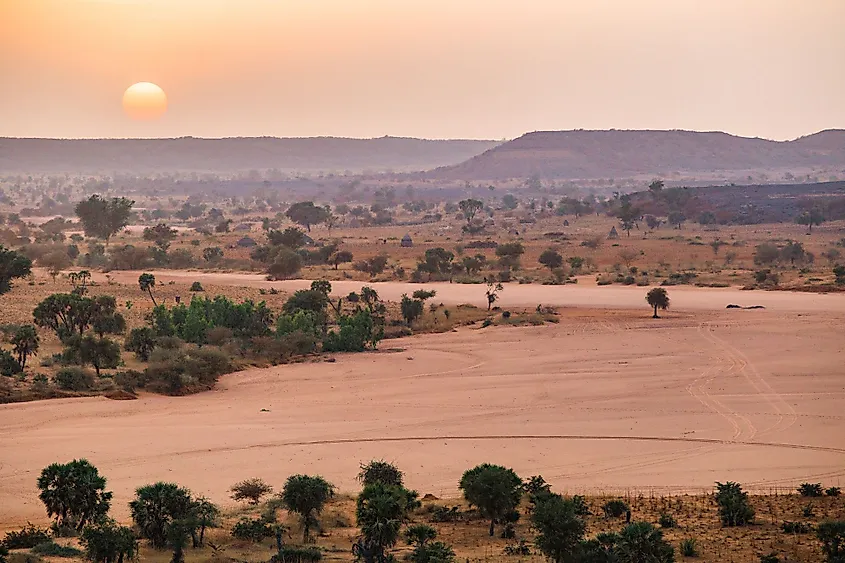
The Sahel, a vast semi-arid region spanning across Africa, is a landscape of striking contrasts. It is a region defined by its geographical position, ecological fragility, and rich cultural heritage. Understanding the Sahel requires navigating a complex interplay of environmental factors, human influence, and historical events. This exploration delves into the Sahel’s geography, its ecological significance, and the challenges and opportunities that define its present and future.
A Band of Transition:
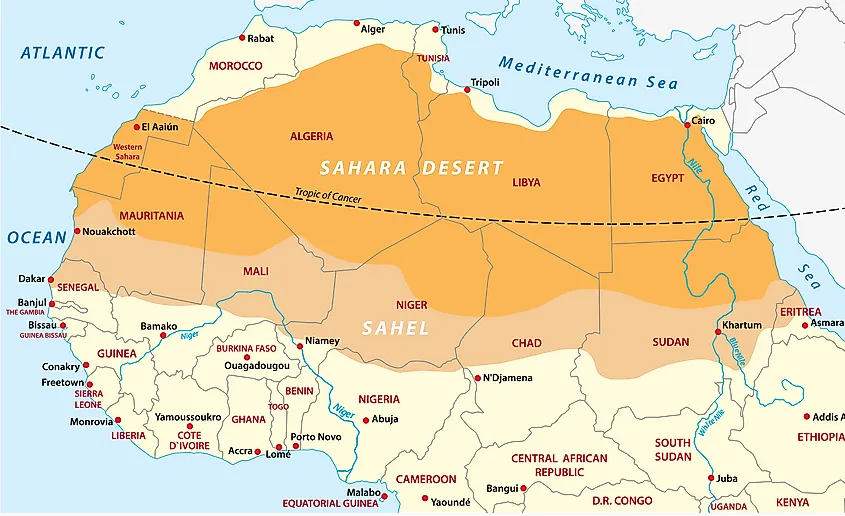
The Sahel acts as a transition zone between the Sahara Desert to the north and the savannas and rainforests of sub-Saharan Africa to the south. This unique position shapes its climate, vegetation, and human interactions. The Sahel stretches across eleven countries, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes, from rolling plains to rocky plateaus, and from dry riverbeds to pockets of lush vegetation.
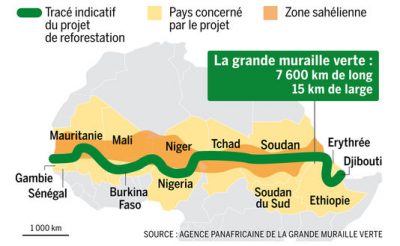
Mapping the Sahel:
A map of the Sahel reveals its geographical extent and the countries it encompasses:
- West Africa: Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Chad
- East Africa: Eritrea, Sudan, Ethiopia, Djibouti, Somalia
The Sahel’s northern boundary is not rigidly defined, as it fluctuates with the shifting edges of the Sahara Desert. The southern boundary is more distinct, marked by the transition to wetter savanna ecosystems.
A Climate of Extremes:
The Sahel’s climate is characterized by a delicate balance between aridity and rainfall. The region experiences a distinct dry season, which can stretch for several months, followed by a shorter rainy season. This variability in rainfall patterns is crucial to the Sahel’s ecology and is a major factor in its vulnerability.
Ecological Significance:
The Sahel is a vital ecosystem that harbors a remarkable diversity of flora and fauna. Despite its aridity, the region sustains a complex web of life, including:
- Vegetation: The Sahel is home to a variety of drought-tolerant plants, including acacia trees, baobab trees, and various grasses. These plants play a crucial role in regulating soil erosion and providing sustenance for local communities.
- Wildlife: The Sahel is a haven for diverse wildlife, including gazelles, antelopes, lions, leopards, and numerous bird species. These animals are adapted to the harsh conditions and contribute to the ecological balance.
- Water Resources: While rainfall is scarce, the Sahel contains valuable water resources in the form of rivers, lakes, and underground aquifers. These resources are essential for human and animal survival, as well as for agriculture.
Challenges of the Sahel:
The Sahel faces numerous challenges that stem from its geographical location, climate, and human activities:
- Climate Change: The Sahel is particularly vulnerable to climate change, with rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall patterns leading to increased droughts, desertification, and land degradation.
- Desertification: The expansion of the Sahara Desert into the Sahel, driven by climate change and unsustainable land use practices, poses a significant threat to the region’s ecosystems and livelihoods.
- Population Growth: Rapid population growth in the Sahel is putting increasing pressure on natural resources, leading to overgrazing, deforestation, and soil degradation.
- Conflict and Instability: The Sahel is prone to conflict, often stemming from competition over scarce resources, political instability, and the presence of armed groups.
- Poverty and Inequality: Poverty and inequality are widespread in the Sahel, exacerbating the region’s vulnerability and hindering development efforts.
Opportunities for Resilience:
Despite the challenges, the Sahel also presents opportunities for resilience and sustainable development:
- Sustainable Land Management: Implementing sustainable land management practices, such as agroforestry, conservation agriculture, and water harvesting, can help mitigate desertification and improve agricultural productivity.
- Renewable Energy: Harnessing the region’s abundant solar and wind energy resources can provide clean and sustainable energy solutions, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting economic development.
- Community-Based Solutions: Empowering local communities to participate in decision-making and implement sustainable practices is crucial for addressing the Sahel’s challenges.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration between governments, international organizations, and local communities is essential for tackling the Sahel’s complex challenges and fostering sustainable development.
FAQs about the Sahel:
1. What is the Sahel’s climate like?
The Sahel experiences a semi-arid climate with a distinct dry season and a shorter rainy season. Rainfall patterns are highly variable, leading to periods of drought and flooding.
2. Why is the Sahel so vulnerable to climate change?
The Sahel’s arid climate and dependence on rainfall make it highly susceptible to climate change. Rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall patterns exacerbate droughts, desertification, and other environmental challenges.
3. What are the main threats to the Sahel’s ecosystems?
The Sahel’s ecosystems are threatened by desertification, driven by climate change and unsustainable land use practices. Overgrazing, deforestation, and soil degradation contribute to the loss of vegetation and biodiversity.
4. How is population growth impacting the Sahel?
Rapid population growth in the Sahel is putting increasing pressure on natural resources, leading to overexploitation, land degradation, and competition for resources.
5. What are some solutions for addressing the Sahel’s challenges?
Addressing the Sahel’s challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, including sustainable land management, renewable energy development, community-based solutions, and international cooperation.
Tips for Understanding the Sahel:
- Engage with maps: Using maps to visualize the Sahel’s geographical extent and the countries it encompasses can enhance understanding.
- Explore online resources: Utilize online resources such as research articles, reports, and documentaries to delve deeper into the Sahel’s challenges and opportunities.
- Support organizations: Consider supporting organizations working to address the Sahel’s challenges through advocacy, research, and development initiatives.
Conclusion:
The Sahel is a region of immense ecological, cultural, and economic significance. It is a vital ecosystem that sustains diverse life, but it is also a fragile landscape facing significant challenges. Understanding the Sahel’s geography, climate, and the interconnected challenges it faces is crucial for implementing sustainable development strategies and promoting resilience. By engaging in informed dialogue, supporting research and initiatives, and fostering international cooperation, we can contribute to a more sustainable future for the Sahel and its people.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Sahel: A Geographical and Ecological Tapestry. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Unraveling The Mystery: Exploring The Bermuda Triangle Through Google Maps
- The Intricate Web Of Territory: Exploring The Map Of The Warrior Cats
- Navigating The Landscape Of Gaming: A Comprehensive Guide To Casinos In New York State
- Unraveling The Secrets Of The Barren River Lake: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Ever-Evolving Landscape Of 2b2t: A Look At The 2021 Map
- Navigating The Terrain Of Conflict: Understanding The Map Of Vietnam During The War
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Fresno: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Geographic Landscape
- Unveiling The Tapestry Of Medieval Spain: A Journey Through Maps
Leave a Reply